Figure 2. The Dnajb1–Prkaca fusion induces FL-HCC in mice.
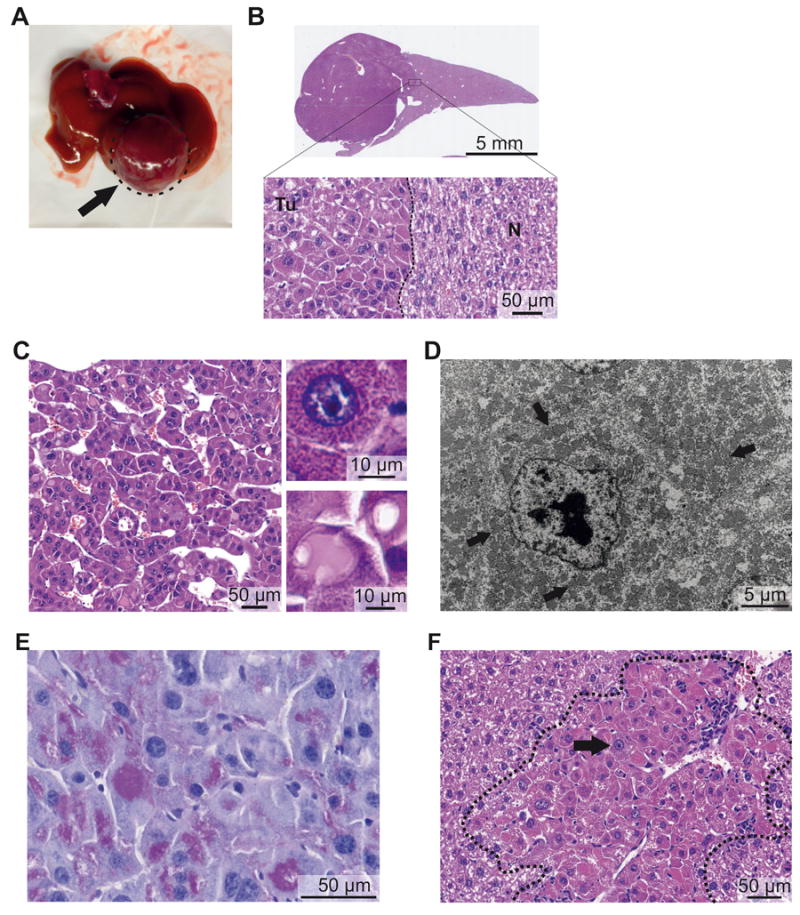
Representative macroscopic and microscopic images of mouse FL-HCC elicited by Dnajb1–Prkaca. (A) Macroscopic image of a tumor (arrow). (B) Whole-scan H&E image and magnification showing tumor (Tu)-non-tumor (N) border. (C) Microscopic H&E image of tumor area showing trabeculae of tumor cells separated by variably dilated sinusoids. (Upper inset) Detail of an “oncocytic” tumor cell with granular eosinophilic cytoplasm and large nucleus with prominent nucleolus. (Lower inset) Detail of “pale body” and hyaline globulus. (D) Transmission electron micrograph of tumor cell showing cytoplasm packed with mitochondria (arrows) and nucleus with prominent nucleolus and coarse chromatin. (E) Periodic acid-Schiff staining of hyaline globules. (F) Small neoplastic lesion with large oncocytic cells with granular eosinophilic cytoplasm and prominent nucleoli (black arrow) and leukocyte infiltration (white arrow).
