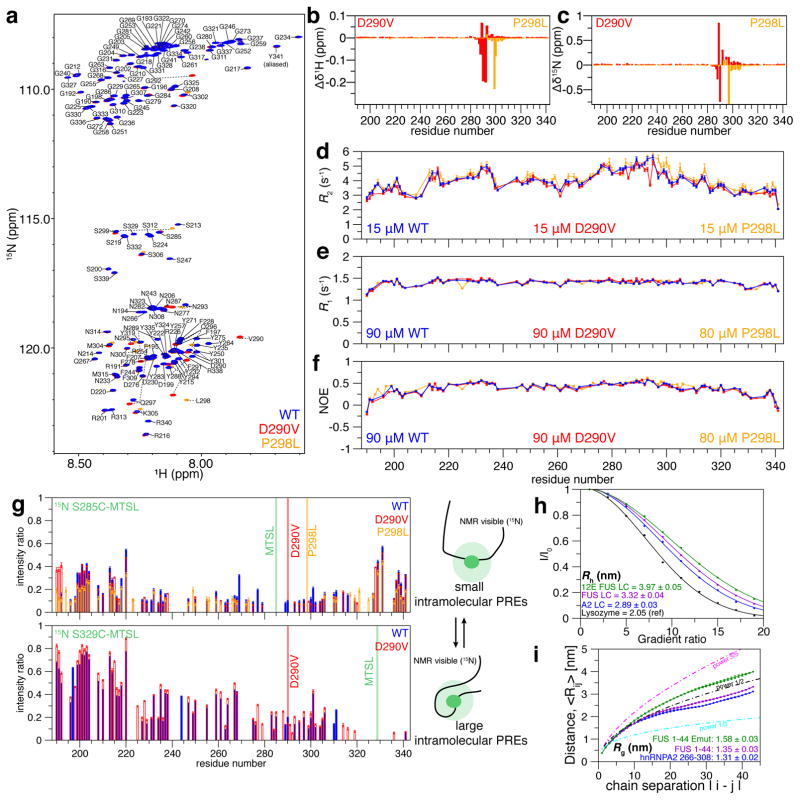
Figure 1. Monomeric LC domain of hnRNPA2 is primarily structurally disordered but compact.
a) 1H-15N HSQC of WT hnRNPA2 LC (blue) is consistent with intrinsic disorder. (b) MSP mutation D290V (red) and (c) PDB mutation P298L (orange) show small chemical shift deviations but do not change the global disorder of hnRNPA2 LC. NMR spin relaxation parameters (d) 15N R2, (e) 15N R1, and (f) hetNOE values for hnRNPA2 LC monomer are consistent with disorder across the entire domain.
g) Consistent with significant transient interactions, extensive intramolecular PRE attenuation after incorporation of a paramagnetic probe at either S285C or S329C occurs across the domain, particularly between residues 220 and 325.
h) PFG NMR diffusion curves for hnRNPA2 LC compared to FUS LC WT and phosphomimetic (12E), and lysozyme. hnRNPA2 LC diffuses faster and thus is more collapsed than FUS LC or its phosphomimetic mutant. Solid line is best-fit solution to I/I0 = Ae−dx2 where d is the diffusion rate constant.
i) Simulated conformational ensemble of hnRNPA2 LC fragment 265–308 is more compact than wild-type or phosphomimetic FUS fragment of the same length (1–44), as judged by intramolecular distance as a function of chain separation and average Rg. Data are mean ± SD. See also Figure S1.