Figure 2.
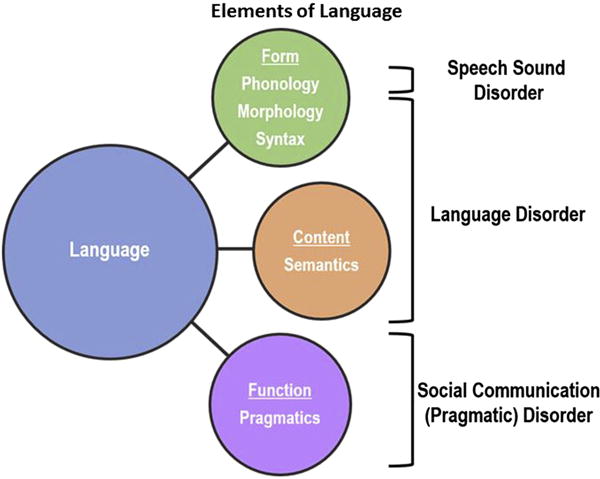
Language disorders affect one or more fundamental aspects of language: form, content, and function. Deficits may involve morphology (understanding and use of the building blocks of words), syntax (grammar), and semantics (vocabulary). Phonology, the ability to distinguish and use speech sounds appropriately, is affected in Speech Sound Disorder. Disorders of pragmatics, the use of language, are encompassed within Social Communication (Pragmatic) Disorder.
