Fig 5.
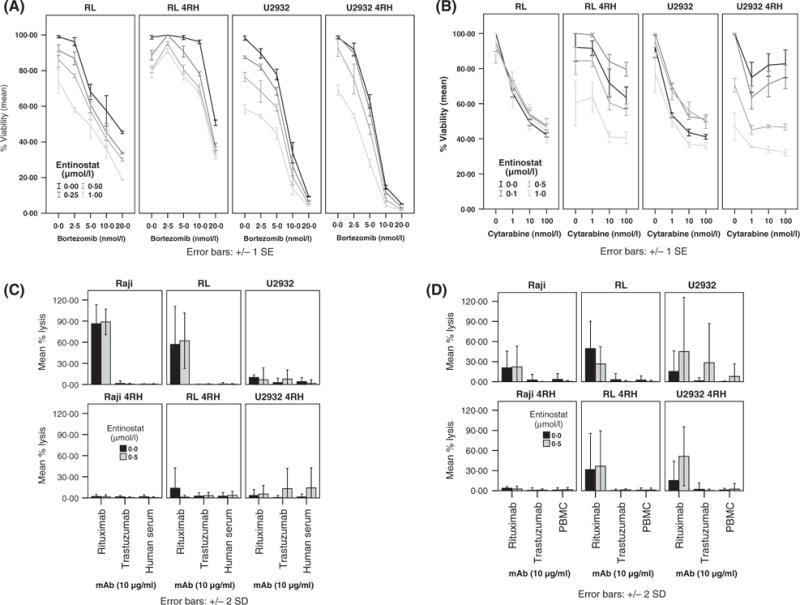
Effects of entinostat on the anti-tumour activity of bortezomib (A), cytarabine (B) or rituximab (C and D) in vitro. Pre-exposure of rituximab-sensitive (RSCL, RL and u2932) or –resistant (RRCL, RL 4RH and U2932 4RH) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cell lines to bortezomib (A) or cytarabine (B) for 24 h enhanced entinostat (0–1 μmol/l) anti-tumour activity. Changes in cell viability were determined using the Cell Titer Glo assay. On the other hand, entinostat (0.5 μmol/l) did not alter rituximab-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC); or (D) complement-mediated cytotoxicity (CMC); (C) in RSCL or RRCL. Cells were exposed to dimethyl sulfoxide or entinostat (5 μmol/l) for 24 h and subsequently labelled with 51Cr. Labelled cells were then exposed to rituximab or isotype (trastuzumab) and peripheral blood mononuclear cells at an effector:target ratio of 40:1 (a) (ADCC) or 20% human serum pooled from healthy volunteers (CMC) and incubated at 37°C, 5% CO2 for 6 h. 51Cr-release was measured and the percentage of lysis calculated.
