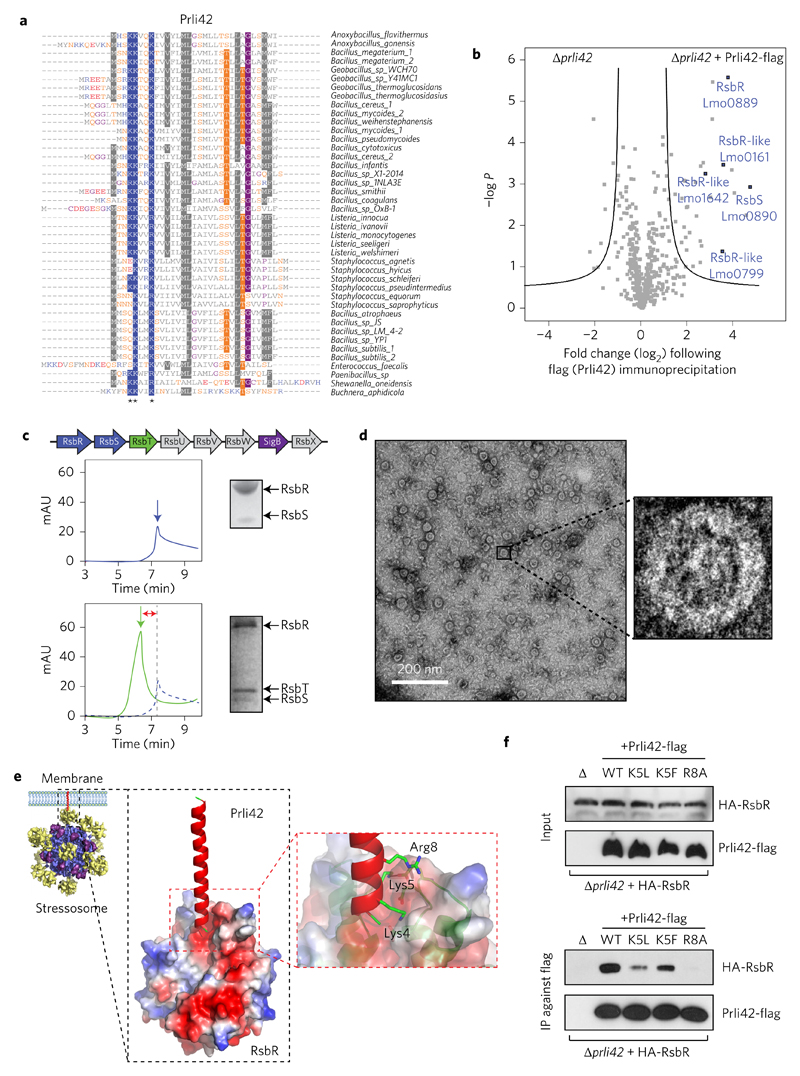
Figure 3. Miniprotein Prli42 is highly conserved and interacts with Listeria orthologues of the stressosome.
a, Multiple sequence alignment of orthologous sequences of Prli42. Amino acids are highlighted when conserved in more than 55% of the sequence. Stars indicate the conserved basic residues (Lys4, Lys5 and Arg8). Colour code for amino acids is as follows: grey, hydrophobic; blue, positively charged; red, negatively charged; orange, neutral; purple, glycine. b, Identification of Prli42 protein interaction partners. The volcano plot shows the intensity fold change (in log2) in the Prli42-expressing strain compared to the control deletion strain on the x axis. The pull-down was performed in triplicate and a t-test was performed to calculate −log P values for each protein, indicated on the y axis. Black lines indicate the boundary of significance as set by Perseus software (FDR = 0.05 and S0 = 1) c, Assembly of the stressosome. The panels show elution from a Superdex-200 sizing column. The RsbR:RsbS complex has an apparent mass of 1.5 MDa (top). The RsbR:RsbS: RsbT complex has an apparent mass of 1.8 MDa (bottom). mAU, milli arbitrary units. d, Electron micrographs of the RsbR:RsbS:RsbT complex, revealing a fourfold symmetry in the central cavity of the supramolecular assembly. e, Model of the Prli42–RsbR interaction from docking of Prli42 to the homodimeric N-terminal domain of Listeria RsbR, obtained through homology modelling from the known N-terminal RsbR structure of B. subtilis (PDB ID: 2BNL). f, WT, K5L, K5F and R8A variants of Prli42-flag were expressed in the Prli42 deletion strain together with HA-RsbR, flag pull-down followed by immunoblotting against the HA-tag. The stressosome was assembled at least three different times, and the elution profiles shown are representative. The experiment in c was subsequently imaged by EM. Immunoblots in f are representative of three independent experiments.