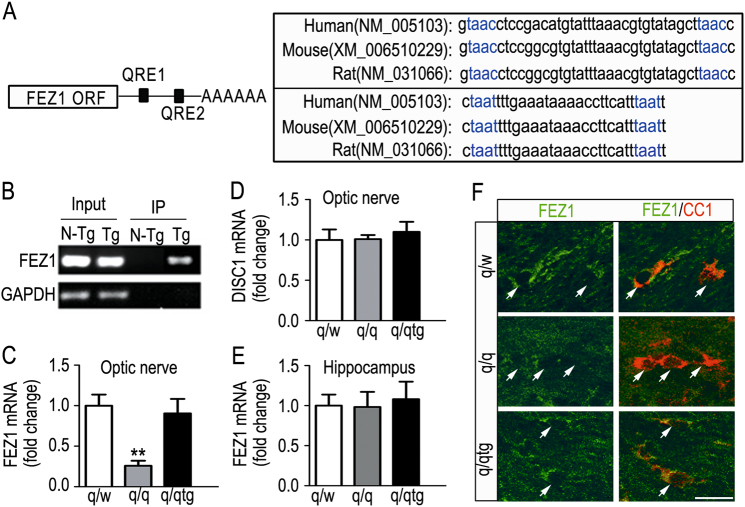
Fig. 5.
Post-transcriptional regulation of FEZ1 mRNA by cytoplasmic QKI. a Schematic illustration (left) of two Quaking response elements (QRE) located at 3’ UTR of FEZ1 mRNA. The QRE motif sequences of human, mouse, and rat QRE motifs are aligned on the right. The consensus QRE sequences are marked in blue. b UV-crosslink immunoprecipitation (CLIP) followed by RT-PCR revealed that interaction of FEZ1 mRNA with Flag-QKI-6 expressed specifically in brain OL of transgenic mice (Tg). Non-transgene (N-Tg) mice were used as a negative control. RT-PCR of the GAPDH mRNA that does not interact with QKI-6 was used as a negative control for specificity. c QKI deficiency in the homozygous quakingviable (qkv) mutant mice (q/q) affects FEZ1 mRNA abundance in OL, which can be rescued by the Flag-QKI-6 transgene. The FEZ1 mRNA levels in optic nerves of qkv/WT (q/w), qkv/qkv (q/q), and q/qtg mice (n = 6) were quantified by RT-qPCR followed by one-way ANOVA analysis and Tukey post hoc test. d RT-qPCR of DISC1 mRNA in the optic nerves of q/w, q/q, and q/qtg mice (n = 4). e RT-qPCR of FEZ1 mRNA in the hippocampus of q/w, q/q, and q/qtg mice (n = 4). f Immunocytochemistry of FEZ1 (green) in mature oligodendrocytes marked by CC1 (red) in the corpus callosum of q/w, q/q, and q/qtg mice. Arrows indicated diminished FEZ1 protein in CC1 + cells from the q/q mice. Scale bar = 25 μm