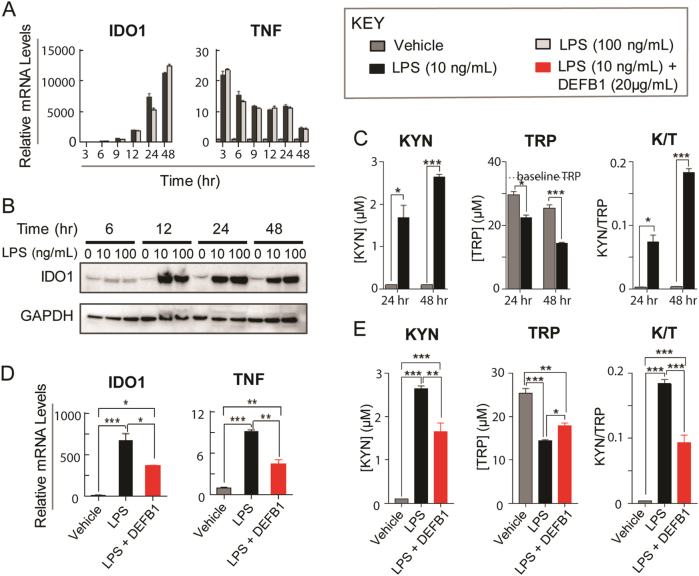
Fig. 4. DEFB1 functional studies in THP-1 cells.
A mRNA expression was determined by qRT-PCR after THP-1 cells were exposed to 10 and 100 ng/ml of LPS at different time points. Compared to vehicle treated cells, IDO1 mRNA levels were significantly increased after LPS treatment. mRNA levels for TNF, a pro-inflammatory cytokine used as a positive control for LPS effect, were also significantly increased after LPS treatment. B IDO1 protein expression was increased as analyzed by Western blot after LPS treatment. C KYN concentrations (left) in cell culture media were undetectable after 24 and 48 h of vehicle treatments, but were significantly increased after 10 ng/ml LPS treatment. At the same time, TRP concentrations (middle) were significantly decreased in cell culture media after LPS treatment and the K/T ratio was increased (right). After 3, 6, or 12 h of LPS treatment, KYN concentrations were undetectable. D mRNA levels for IDO1 and TNF were significantly increased after 10 ng/ml LPS treatment, but recombinant human DEFB1 co-incubation with LPS significantly decreased mRNA levels for IDO1 and TNF when compared with LPS treatment alone. E When DEFB1 was co-incubated with LPS as compared to LPS alone, KYN concentrations (left) in cell culture media were significantly decreased, TRP concentrations were increased (middle) and K/T ratios (right) were decreased after DEFB1 was pre-incubated with LPS when compared with results for cells treated with LPS alone. N ≥ 3 for all the experiments. Data = mean ± SEM, with statistical significance determined by two-tailed t-test denoted as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001