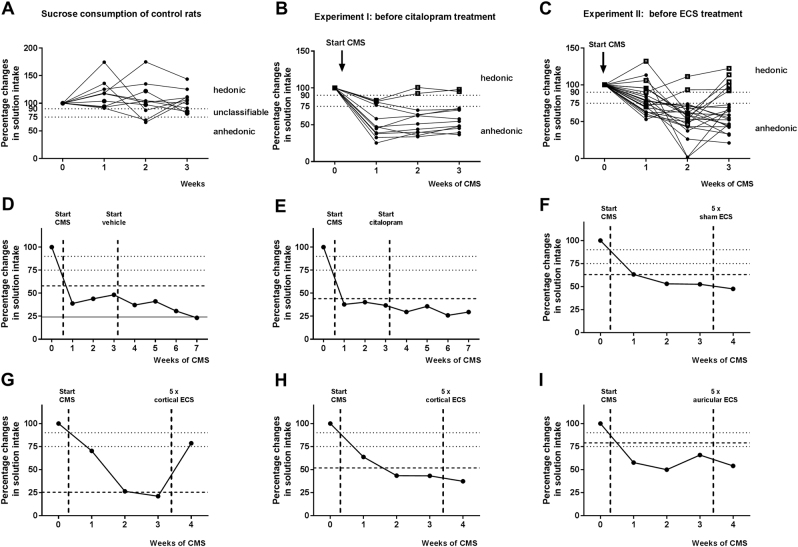
Fig. 2.
Individual responses to chronic mild stress (CMS) and antidepressive treatments in the sucrose consumption test in rats. a Illustrates that sucrose consumption survey over 3 weeks in unstressed control rats results in 8 out of 10 rats with hedonic-like behavior, whereas 2 rats were unclassifiable. b Data from experiment I, showing that 3 weeks of CMS induced anhedonic-like behavior in 10 out of 15 animals. Thus, the number of anhedonic-like rats was increased after CMS compared with unstressed controls (P = 0.0024). Hedonic-like behavior was present in 2 out of 15 animals. c Data of experiment II, showing that 3 weeks of CMS-induced anhedonic-like behavior in 17 out of 29 rats. Thus, the number of anhedonic-like rats was increased after CMS compared with unstressed controls (P = 0.0015). Hedonic-like behavior was present in 6 out of 29 rats. Small dashed lines represent threshold for selection of hedonic- and anhedonic-like rats (anhedonic-like rats > 25% within-subject decrease in sucrose consumption, hedonic-like rats < 10% within-subject decrease in sucrose consumption). d–i Representative data from individual rats following different types of antidepressive treatment. d A vehicle-treated rat from experiment I; e a citalopram-treated non-responder from experiment I; f a rat from experiment II after five sham ECS sessions; g a responder from experiment II after five cortical ECS sessions; h a nonresponder from experiment II after five cortical ECS sessions; and i a nonresponder from experiment II after five auricular ECS sessions. Responses of all treated rats are shown in Table 1. Wide dashed lines represent the threshold for positive response and solid lines represent threshold for negative treatment response. See Figs. S1–S5 for data of all individual rats