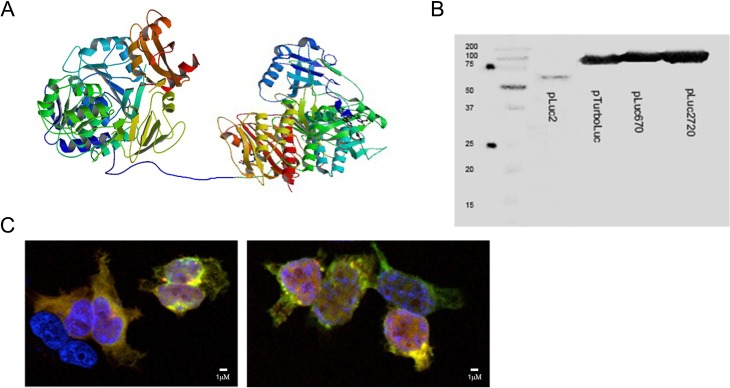
Fig. 1.
Generation of new fusion luciferase (luc2) reporters with near infrared fluorescence proteins. (A) Schematic drawing of the luc2 fusion with iRFP720 via a 14-aa linker. Photinus pyralis luc2 (PDB ID code 1LCI) and Chromophore-binding domain (CBD) of bacterial phytochrome RpBphP2 (PDB ID code 4E04) were used. (B) Western blot results using an anti-luc2 primary antibody on human embryonic kidney (HEK)-293 lysates used for transient expression of the proteins. The band in the first lane corresponds to luc2 protein (62 KDa), the second to the TurboLuc protein (∼88 KDa). The third and fourth lanes correspond to luc2-iRFP670 (abbreviated pLuc670) and luc2-iRFP720 (abbreviated pLuc2720; ∼97 KDa). (C) Immunofluorescence for the analysis of colocalization of luc2 (green signal) and near infrared proteins (red signal) in HEK-293 cells. Nuclei are stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (blue signal). luc2 was detected using an anti-luc2 antibody and Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled secondary antibody. Near infrared proteins were detected using a 633-nM excitation laser. Image on the left corresponds to cells expressing luc2-iRFP670 and image on the right corresponds to cells expressing luc2-iRFP720.