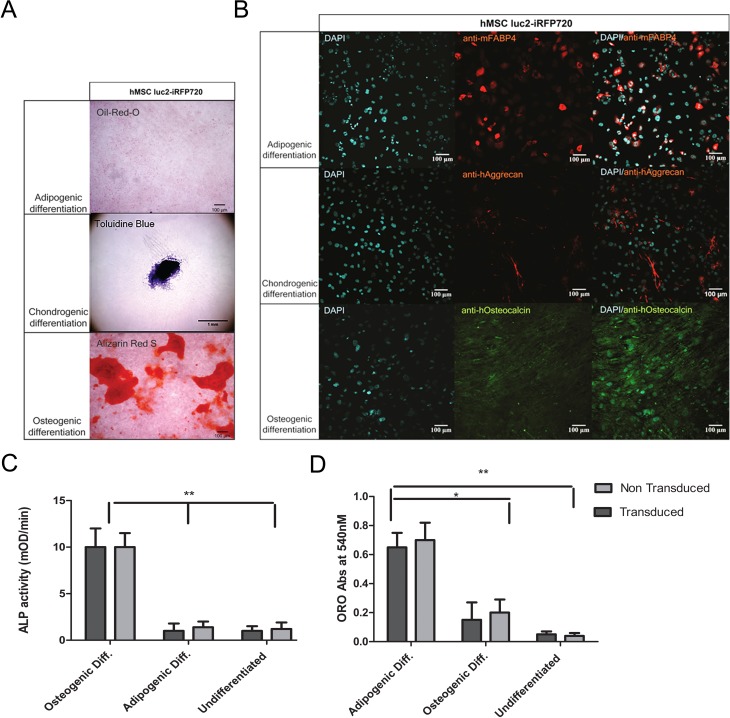
Fig. 4.
Histological staining and immunofluorescent staining of luc2-iRFP720 expressing human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) in determining differentiation capabilities. (A) Oil Red O staining showed the presence of fat deposition, toluidine blue staining showed the presence of proteoglycans, and alizarin Red S showed the presence of calcific deposition after adipogenic, chondrogenic, and osteogenic differentiation of luc2-iRFP720 expressing hMSCs, respectively. (B; left column) 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining showed cell nuclei, (middle column) hMSC luc2-iRFP720 showed immunofluorescent staining of anti-mouse fatty acid binding protein 4 (anti-mFABP4), anti-human aggrecan (anti-hAggrecan), and anti-human osteocalcin (anti-hOsteocalcin) after conditioned adipogenic, chondrogenic, and osteogenic differentiation, respectively. (Right column) Merged images of DAPI and the specific antibody (n = 3). (C) alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity measured in medium of luc2-iRFP720 expressing hMSCs, and non transduced hMSCs after 14 d of adipogenic or osteogenic ALP activity during osteogenic differentiation are significantly higher (P < 0.01) than during adipogenic differentiation or undifferentiated control cells. (D) Oil Red O absorbance values at 540 nM suggest that the level of adipocytes in different culturing conditions is not affected by transduction, but it is significantly higher in adipogenic differentiation compared to osteogenic differentiation or undifferentiated cells (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01).