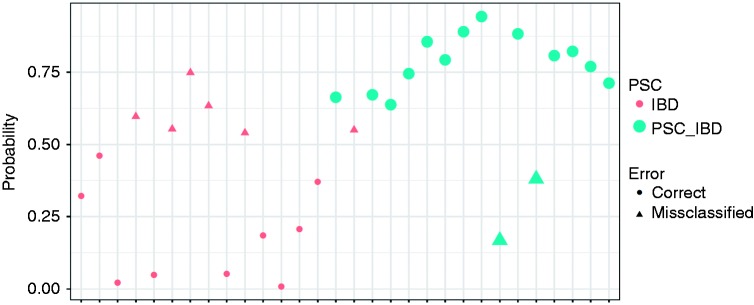
Figure 1.
Results of the linear discriminant analysis allowing to see the discrimination of primary sclerosing cholangitis associated with inflammatory bowel disease (PSC-IBD) versus inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) alone, based on the combination of the main bile acids (BAs) present in stool (cholic acid (CA), chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA), litocholic acid (LCA), deoxycholic acid (DCA) and ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA)). On the x axis each marker represents a patient. On the y axis is represented the probability of being correctly classified as PSC-IBD using the BA analytes. The green markers represent patients with PSC-IBD and the pink markers represent patients with IBD. The circles represents patients that were correctly assigned to their disease group. The classification accuracy of the linear discriminant analysis (LDA) was 73%, with a sensitivity and specificity of 86.7% and 60% respectively.