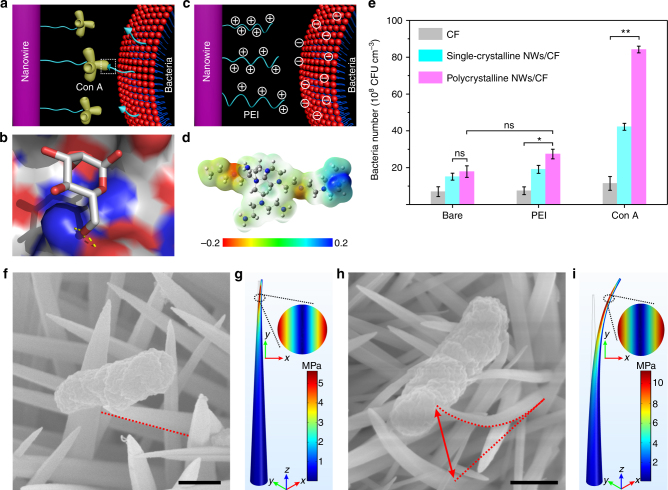
Fig. 4.
Characterization of 3D nanoclaws formation. a Con A on NW surfaces bound to mannose on the bacterial membrane. b The graph shows the hydrogen bonds (yellow sticks) in the crystal structure of the binding site of mannose to Con A (PDB code 1i3h) using the PYMOL software. c Illustration of electrostatic interactions between the cationic polymer of PEI modified on NW surfaces and bacterial membranes. d An electrostatic potential map for a representative conformation of PEI. e Comparing the bacterial capturing capacity of different molecules modified on NW surfaces at a flow velocity of 10 cm s−1. Error bars: standard error (n = 3). Student’s t-test, **P < 0.01; ns, not significant. f–i SEM measurements and FEM simulations for the deflection distance of NWs after bacterial capture, f single-crystalline and h polycrystalline NWs of SEM images. The von Mises stresses of g a single-crystalline and i a polycrystalline NW concentrated at the NW tips under constant displacements of 100 nm and 1 μm, respectively. A 2D diagram corresponding to the von Mises stress at a height of 4.5 μm (inset). Scale bars in f and h are 500 nm