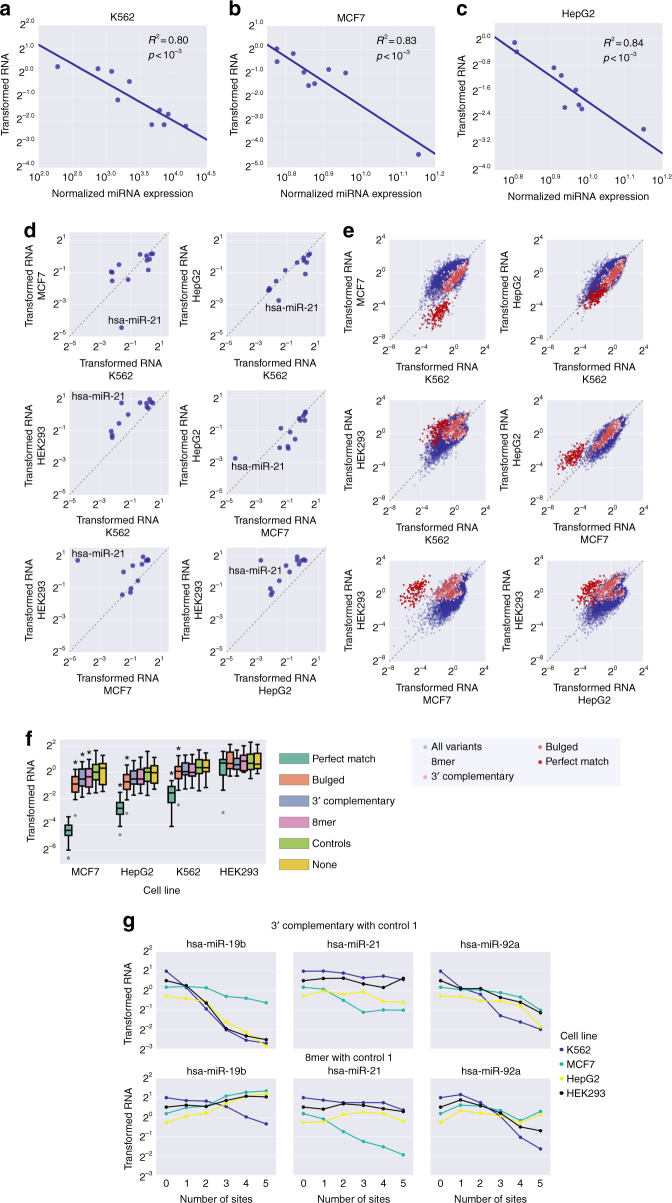
Fig. 8.
Varying miRNA profiles across cell lines affect reporter expression. a–c The median-transformed reporter RNA levels for perfect match MREs (see also Supplementary Figure 9) as a function of the miRNA expression levels, as quantified by published microarray for K56234, MCF745, and HepG246, for the ten selected miRNAs. Calculated R2 and associated p-values are indicated. For MCF7 and HepG2, hsa-miR-223 was excluded from this analysis due to its extremely low expression. d Pairwise comparison of transformed reporter RNA levels for perfect match MREs (see also Supplementary Figure 9) for the ten selected miRNAs. Hsa-miR-21 is annotated in every subplot. e Pairwise comparison of transformed RNA levels for all measured reporter library variants. The colored points indicate different MRE types for hsa-miR-21 as shown in the legend. f Transformed RNA levels of reporter constructs with different MRE types for hsa-miR-21 in different cell lines. Controls contain control sequences instead of the MRE. The "None" group contains the context with no inserted sequences. Boxplots marked with * are significantly different (p < 0.05, Mann–Whitney U one-sided test) from the controls group. See also Supplementary Fig. 10. g Transformed RNA levels as a function of number of MRE sites for K562, MCF7, HepG2, and HEK293 cells. Analysis was performed as in Fig. 4e per cell line. Plots shown are for 3′ complementary with control 1 and 8mer with control 1 at the top and bottom rows, respectively. Colors represent results from different cell lines as shown in the legend. A stronger effect is observed for hsa-miR-21 in MCF7 cells, where it has the strongest activity. See also Supplementary Fig. 11