Fig. 6.
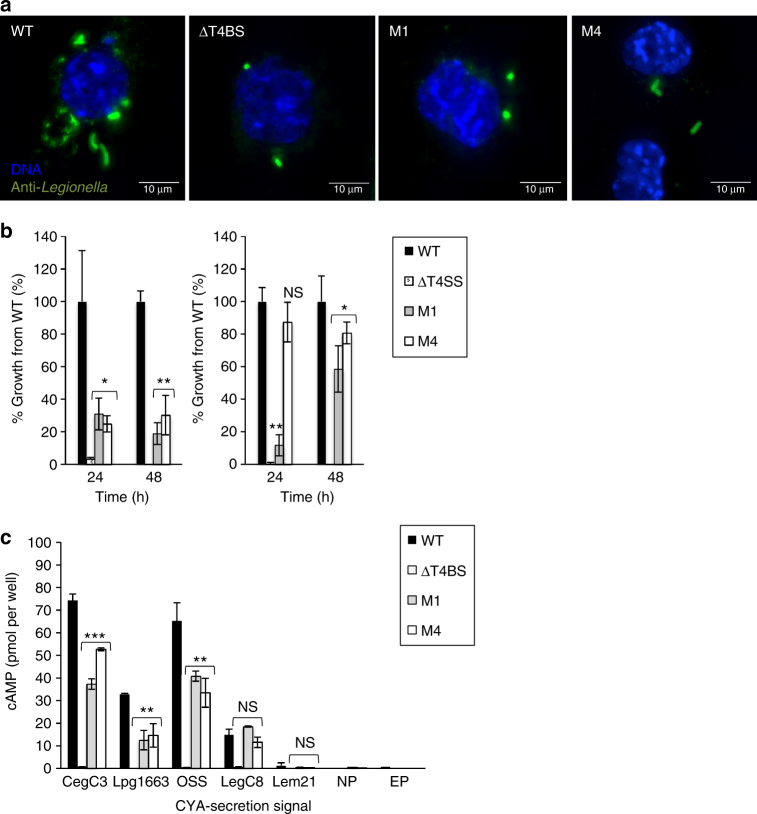
Survival and transfer activity of binding-defective DotM Legionella mutants. a J774A.1 mouse macrophage-like cells were infected for 2 h with wild-type (WT) L. pneumophila (Lp01), T4BS system-deficient L pneumophila (ΔT4BS) or isogenic strains containing the indicated dotM mutations (M1 or M4), and fixed using 4% PFA. Bacteria were stained with anti-L. pneumophila antibody and a secondary antibody labeled with Alexa fluor 488 (green), while the host cell DNA was stained using DAPI (blue). Stacked images are shown in each panel. Bar = 10 μm. b Intracellular growth of L. pneumophila strain Lp01 and isogenic strains producing the binding-defective DotM proteins M1 and M4. The intracellular growth of these L. pneumophila strains were determined in J774A.1 cells (left panel), and the protozoan host A. castellanii (right panel) as described in Methods. Graphs report colony-forming units ± standard deviation for each strain as percentages compared to wild-type. Bacteria were counted after either 24 or 48 h post infection as described in Methods. *, **, and *** indicate P values <0.05, <0.01, and <0.001, respectively. c Translocation of Cya fusions by L. pneumophila into host eukaryotic cells. The ability of various effectors C-terminal translocation signals to translocate a reporter Cya was monitored in DotM wild-type or binding-defective mutants Legionella backgrounds by measuring cAMP levels in host cells 90 min after infection as described in Methods. Translocation levels are shown for the L. pneumophila wild-type (WT) strain, the T4BS system-defective strain (ΔT4BS), and the L. pneumophila dotM mutants M1 and M4, as well as for bacteria without a plasmid (NP) and with unfused Cya (EP; shown only for WT). *, **, and *** indicate P values <0.05, <0.01, and <0.001, respectively