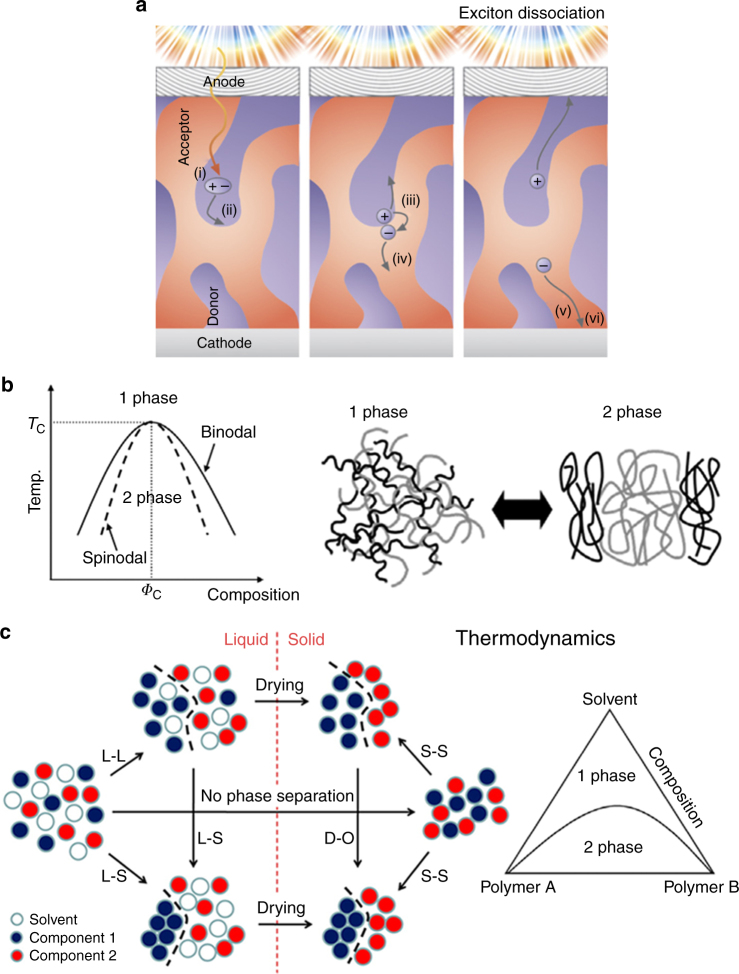
Fig. 3.
Phase separation of multicomponent systems. a Diagram of the OPV operation, which consists of (i) excitation by a photon, (ii) migration of an exciton to a donor–acceptor interface, (iii) exciton dissociation by charge transfer, (iv) charge separation, (v) migration to the electrode, and (vi) charge extraction. One key to effective energy harvesting is the effective dissociation of coulombically bound excitons at the domain boundaries separating the donor and acceptor before the exciton recombines. The exciton diffuses on average about 10 nm before it recombines, thus implying that the optimal domain size should be around the same length scale. The thermodynamic phase diagrams describing a simple two-component polymer system (b) and a ternary diagram addressing the role of the solvent (c). Multiple processes can occur as the non-equilibrium state of the drying film’s microstructure evolves, and therefore overall film evolution is likely a combination of both kinetically limited and thermodynamically limited processes. Figures adapted from ref. 108 (copyright 2010 IOP Science), ref. 127 (copyright 2014 MDPI), and ref. 114 (copyright 2013 American Chemical Society)