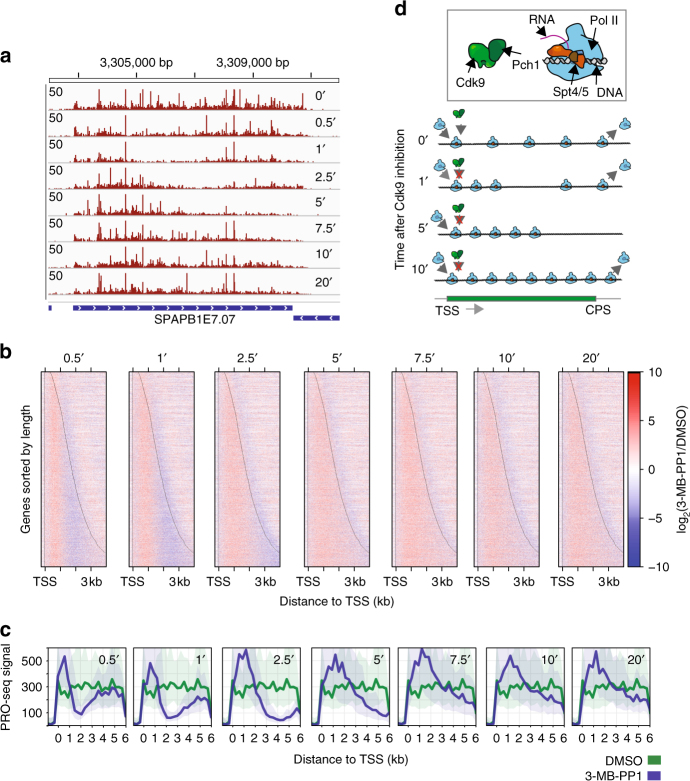
Fig. 3.
A checkpoint during early elongation impacts Pol II rates. a Browser track image displaying the normalized PRO-seq read count signal at the SPBAPB1E7.07 locus for cdk9as cells treated with 10 μM 3-MB-PP1 for an increasing duration, from top to bottom. b Heat maps of log2(treated/untreated) normalized PRO-seq signal within 10 bp windows from −250 bp to +4000 bp around the TSS for all filtered genes (n = 3383) ordered by increasing gene length from top to bottom. Panels show PRO-seq data from each time point of drug treatment (relative to the 0-min sample), with increasing duration from left to right. c Composite PRO-seq signal for all filtered genes at least 6 kb in length (n = 42) before and after treatment. Panels from left to right show profiles after increasing duration of treatment compared with DMSO-treated cells. Data used in a–c reflect the results of combined data from two biological replicates for each treatment. d Illustration of two populations of transcribing Pol II, which have rates differentially affected by Cdk9 inhibition