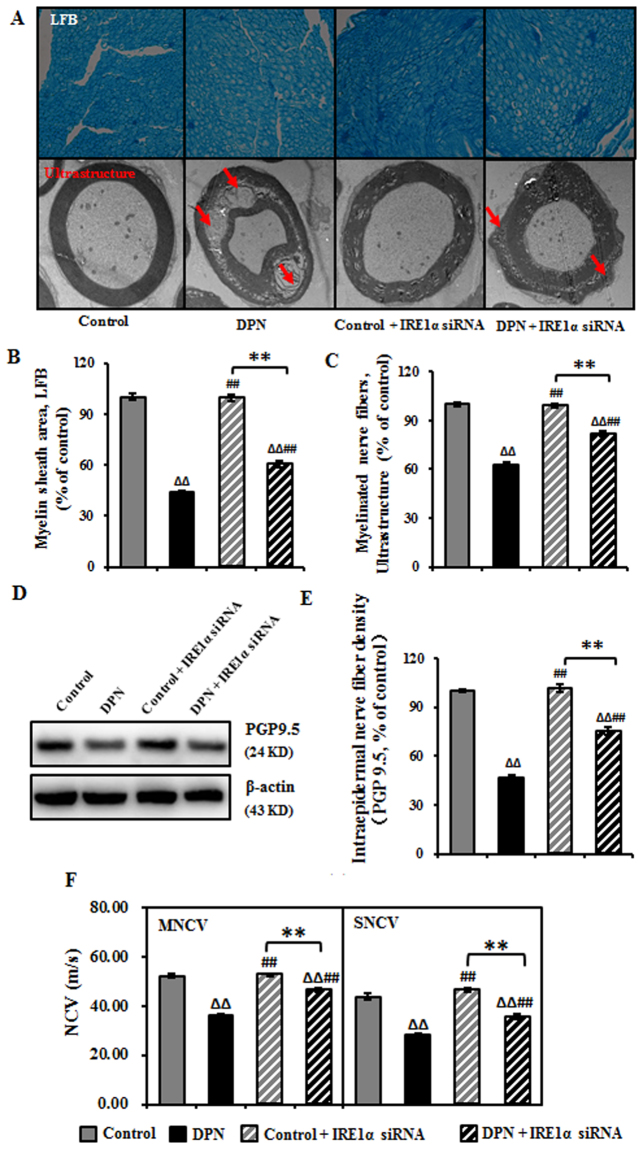
Figure 2.
Improved neurological morphology and function of sciatic nerve in DPN rats after the intrathecal injection of IRE1α siRNA. (A) Transfection of IRE1α siRNA increased the myelin sheath area and myelinated nerve fibers in DPN rats. Representative pictures of Luxol fast blue (LFB) staining (magnification 40×) of myelin sheath and ultrastructure (magnification 6000×) of myelinated nerve fibers. (B) Myelin sheath area expressed as mean ± SEM of the percentage of the respective controls and analyzed using one-way ANOVA with LSD analysis or unpaired Student’s t-test. (C) The number of myelinated nerve fibers expressed as mean ± SEM of the percentage of the respective controls and analyzed using one-way ANOVA with LSD analysis or unpaired Student’s t-test. (D) Representative Western blots using tissue extracts from the sciatic nerve and probed with antibodies against PGP9.5. β-actin was probed as loading control. (E) The intensity of PGP9.5 expressed as mean ± SEM of the percentage of the respective controls and analyzed using one-way ANOVA with LSD analysis or unpaired Student’s t-test. (F) NCV reported as mean ± SEM and analyzed using one-way ANOVA with LSD analysis or unpaired Student’s t-test. ΔΔP < 0.01, compared to control; ##P < 0.01, compared to DPN; **P < 0.01 (N = 6 per group).