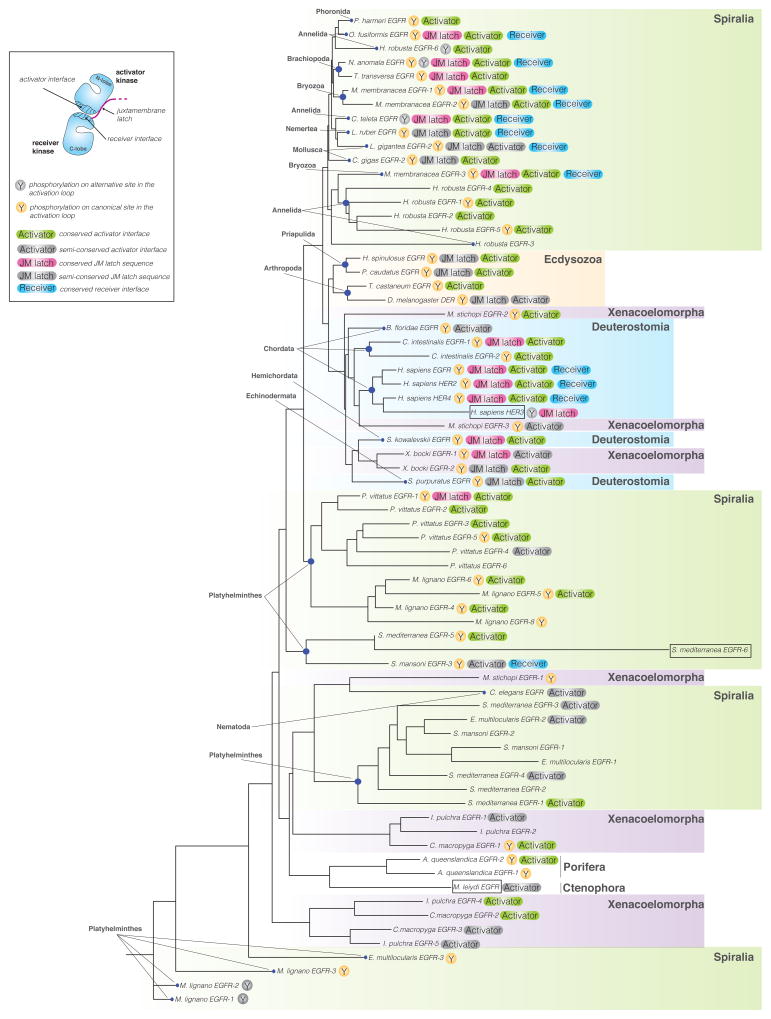
Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree of EGFR kinase domain protein sequences in the animal kingdom.
The tree was assembled from 71 sequences representing EGFR kinase domains in 30 different species aligned using MUSCLE 3.7 (Edgar, 2004). The tree was built using the phylogeny software PhyML 3.0 based on the maximum likelihood principle (Anisimova and Gascuel, 2006; Dereeper et al., 2008). Degrees of protein sequence conservation in the regions corresponding to the allosteric activator interface (Activator), receiver interface (Receiver), and the juxtamembrane latch (JM latch) are indicated by different colors. EGF receptors predicted to be inactive are marked by boxes. See also Tables S1 and S2.