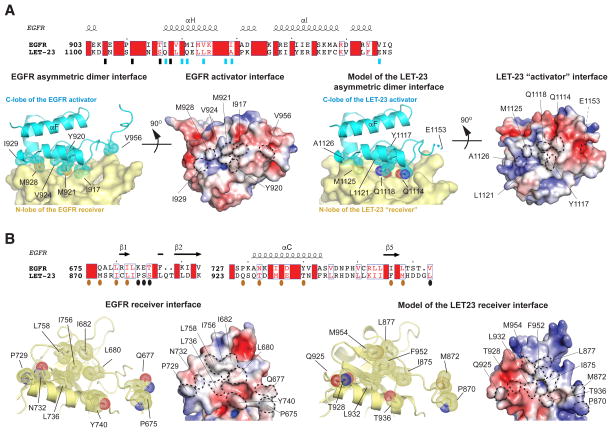
Figure 4. Structural analysis of the LET-23 asymmetric dimer model.
(A) Upper panel - sequence alignment of LET-23 and human EGFR kinase domain within the region containing residues involved in the activator interface. Residues in the activator interface are denoted by rectangles, which are blue if the residues are depicted on cartoon images in lower panels. Lower panels – detailed view of the asymmetric dimer interface in the human EGFR kinase dimer (PDB ID: 2GS6) (left panels), and in the homology model of the LET-23 asymmetric dimer (right panels). The key interfacial residues on the activator interface are shown in stick and dot representation. Residue E1153 in the LET-23 C-lobe was included in the original structure, but removed during generation of the homology model, likely due to unfavorable interactions with the LET-23 N-lobe in the asymmetric dimer model. (B) Upper panel - sequence alignment of LET-23 and human EGFR kinase domain within the region containing residues involved in the receiver interface. Residues in the activator interface are denoted by ovals, which are dark orange if the residues are depicted on cartoon images in lower panels. Lower panels – detailed view of the receiver interface of the active human EGFR kinase dimer (PDB ID: 2GS6) (left panels), and in the homology model of the LET-23 asymmetric dimer (right panels). The key interfacial residues on the activator interface are shown in stick and dot representation. The electrostatic surface potentials shown for the activator and receiver interfaces were calculated using APBS (Baker et al., 2001).