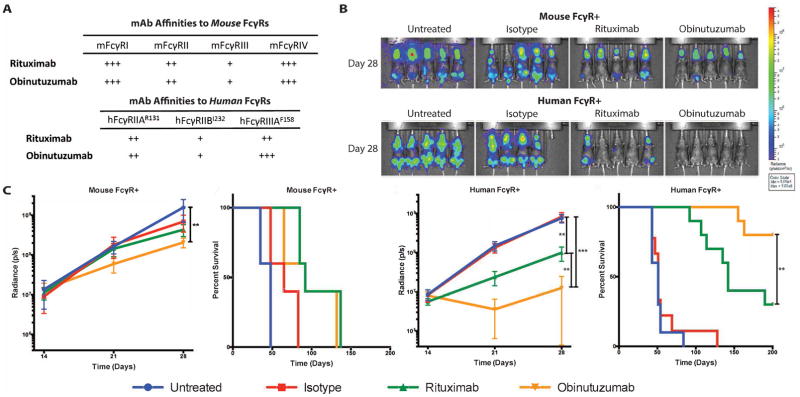
Figure 2. The human FcγR+ RHuFR1− mouse is superior to the conventional Rag2−/− mouse in replicating rituximab versus obinutuzumab clinical outcomes.
(A) Relative affinities of the relevant mouse and human FcγRs. (B) Bioluminescence imaging of Rag2−/− mouse FcγR+ and RHuFR1− female mice at day 28. (C) Left two curves show total radiance signal (photons/second) and Kaplan-Meier survival curves for Rag2−/− mouse FcγR+ mice (n=5 mice/group). Obinutuzumab therapy resulted in a small reduction in overall tumor burden when compared to untreated mice (p=0.0072) and no difference in survival was observed between the two anti-CD20 mAb therapy groups. Right two curves show total radiance signal (photons/second) and Kaplan-Meier survival curves for all RHuFR1− mice (n= 9–10 mice/group). Obinutuzumab therapy demonstrated significant reductions in tumor burden compared to untreated and isotype (p<0.0001 for both). There was also a significant difference in overall tumor burden between rituximab and obinutuzumab treated groups (p=0.003) and a significant survival advantage for obinutuzumab therapy compared to rituximab therapy (p=0.0088).