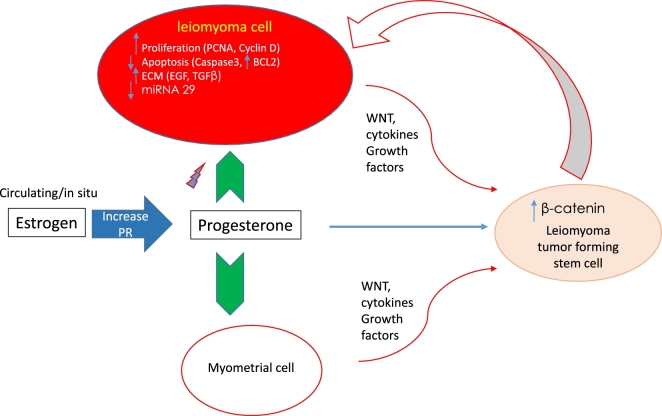
Figure 1.
Role of progesterone in uterine fibroids pathogenesis. Progesterone, in response to estrogen, affects different cellular functions such as proliferation, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix deposition, either directly on fibroid cell via progesterone receptors or indirectly via paracrine effect on fibroid stem cells which give rise to more fibroid cells. Abbreviations: PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; BCL2, B-cell lymphoma 2; ECM, extracellular matrix; EGF, epidermal growth factor; TGFβ, transforming growth factor β; PR, Progesterone receptor.