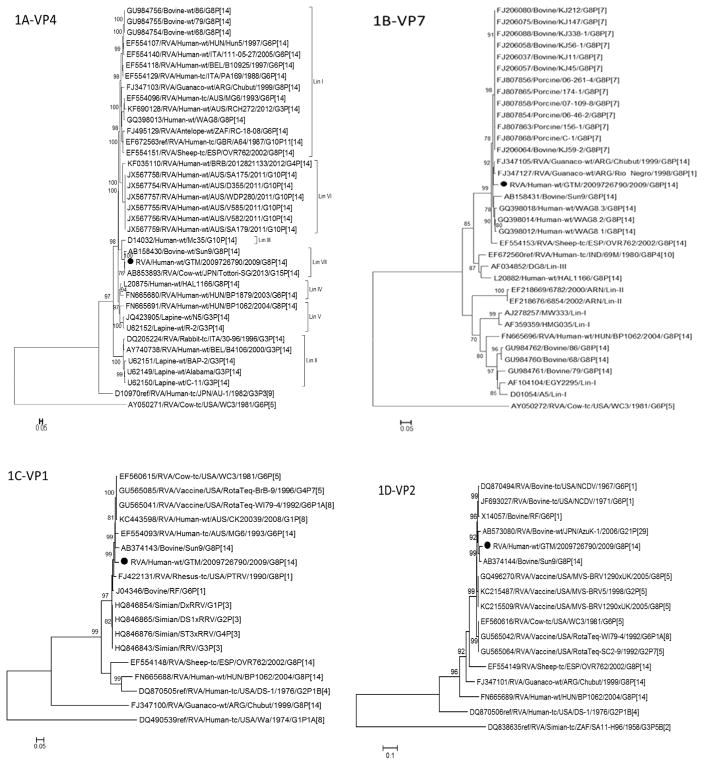
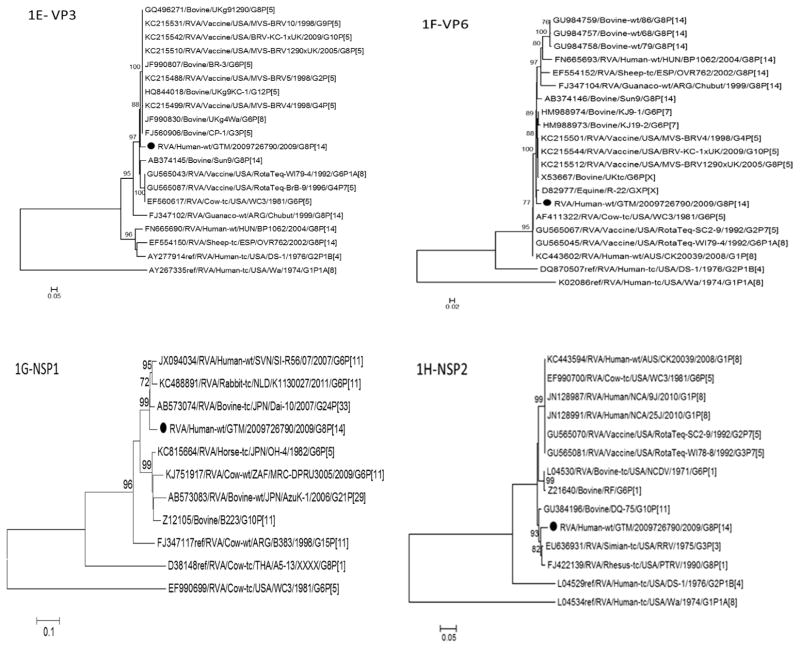
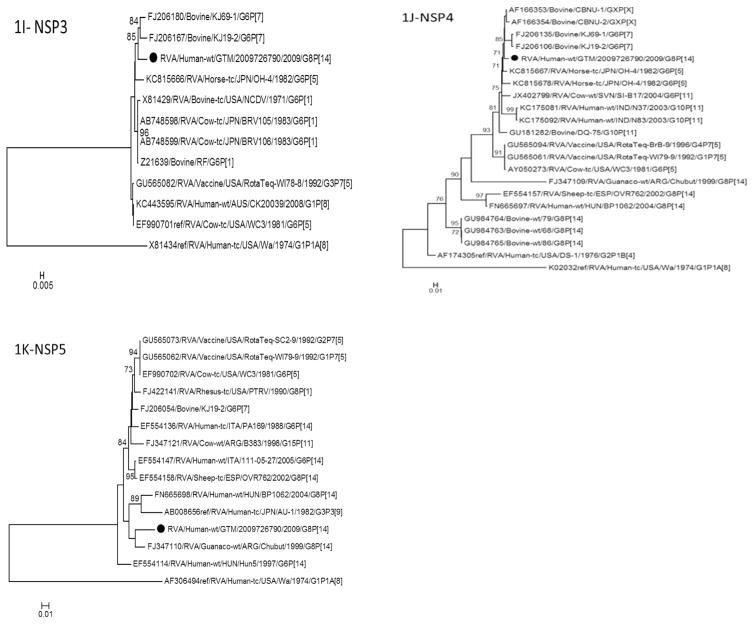
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic trees based on nucleotide sequences of complete open reading frames of 1A-VP4, 1B-VP7, 1C-VP1, 1D-VP2, 1E-VP3, 1F-VP6, 1G-NSP1, 1H-NSP2, 1I-NSP3, 1J-NSP4 and 1K-NSP5 rotavirus genes. The maximum likelihood trees were constructed using PhyML 3.0 with best model identified by J ModelTest2 program for each gene (NSP1-GTR + 1 + G; NSP2-TIM2 + I; NSP3-TIM2 + I; NSP4-TPM2uf + G; NSP5-HKY + G; VP1-TIM2 + I; VP2-GTR + I; VP3-TIM1 + I; VP4-GTR + G; VP6-TrN + G; VP7-TVM + G). The GenBank accession numbers, strain names and G and P-type associations are shown where available.