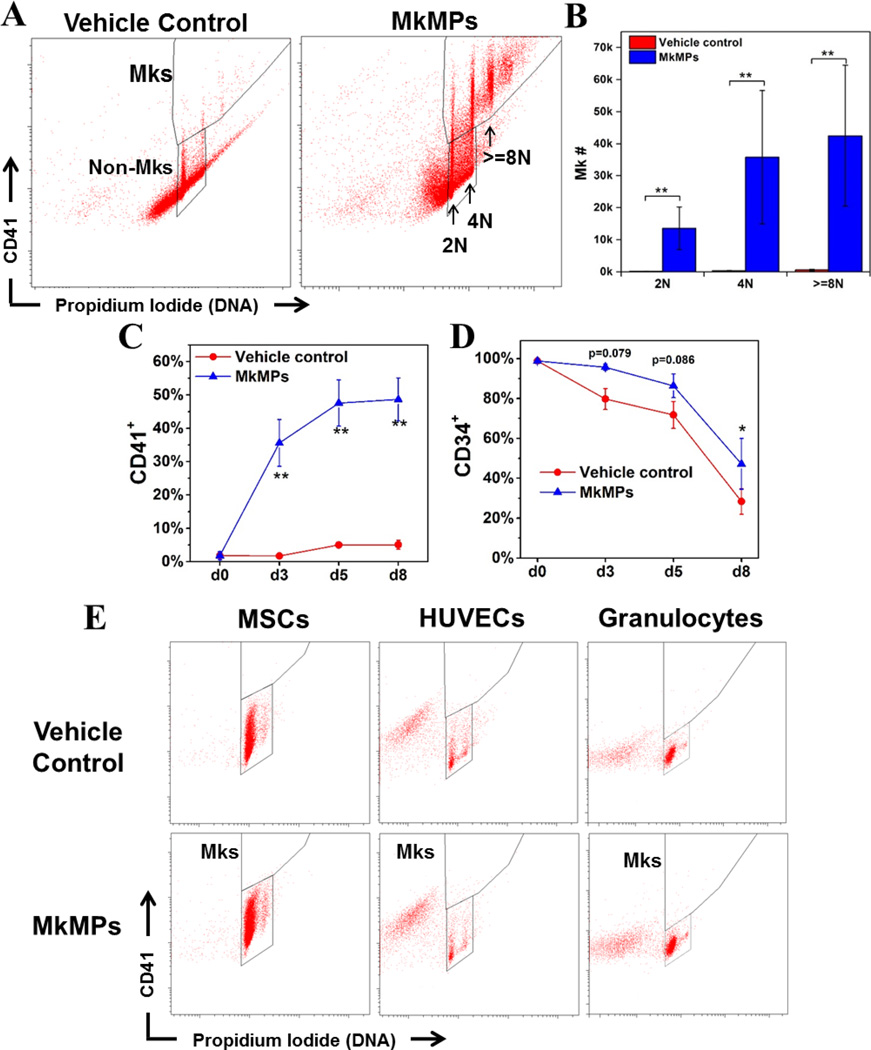
Fig. 2. MkMPs promote Mk differentiation of primitive Lin CD34+ stem cells and this effect is target specific for HSPCs.
60,000 primitive Lin HSPCs were enriched from CD34+ cells and cocultured with MkMPs at concentration of 10 MkMPs/cell for 8 days. (A) Representative flow cytometric CD41 expression and ploidy analyses of cells from vehicle control cultures and the MkMP cocultures at d8. (B) Numbers of Mks with different ploidy classes (2N, 4N and >=8N) in vehicle control cultures and the MkMP cocultures at d8. Percentages of (C) CD41+ and (D) CD34+ cells in vehicle control cultures and the MkMP cocultures at d0, d3, d5 and d8. (E) Representative CD41 expression and ploidy analyses of two sets of MkMP cocultures with MSCs, HUVECs or granulocytes. Human MSCs (passage 2–4), HUVECs (passage 3–5) and CD34+ cell-derived granulocytes (d7 of culture) were cocultured with MkMPs at the concentration of 10 MkMPs/cell for 8 days before being harvested for CD41 expression and ploidy analyses. The data in panels (B–D) are represented as the average of three biological replicates ± standard error of mean. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01.