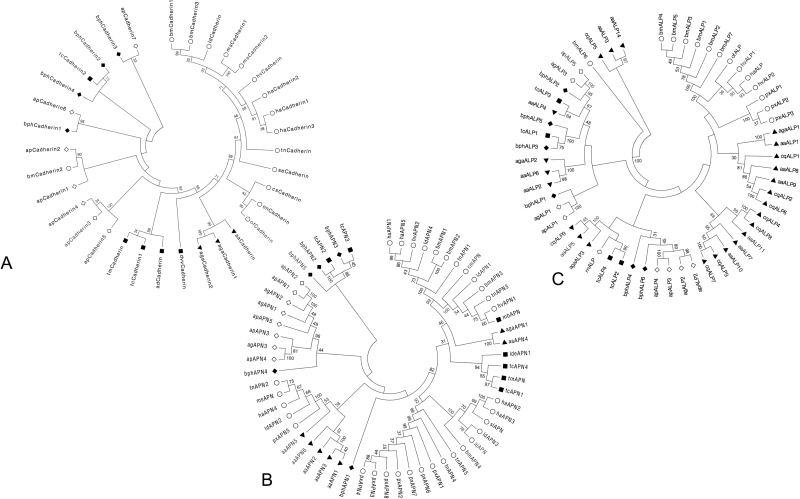
Fig. 1.
Molecular phylogenetic analysis of selected cadherins (A), APNs (B), and ALPs (C) from BPH transcriptome by maximum-likelihood method. Amino acid sequence alignment for each analysis was conducted by the MEGA 6.06 built-in MUSCLE program followed by the screening of conserved blocks by the Gblocks program. The evolutionary history was inferred by using the maximum-likelihood method based on the Le_Gascuel_2008 model (Le and Gascuel 2008). The bootstrap consensus tree inferred from 1,000 replicates (Felsenstein 1985) is taken to represent the evolutionary history of the taxa analyzed (Tamura et al. 2013). Initial trees for the heuristic search were obtained by applying the neighbor-joining method to a matrix of pairwise distances estimated using a JTT model. A discrete gamma distribution was used to model evolutionary rate differences among sites [four categories (+G, parameter = 3.2778)]. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA 6.06. Information about amino acid sequences included in each tree is shown in Additional Table 9.