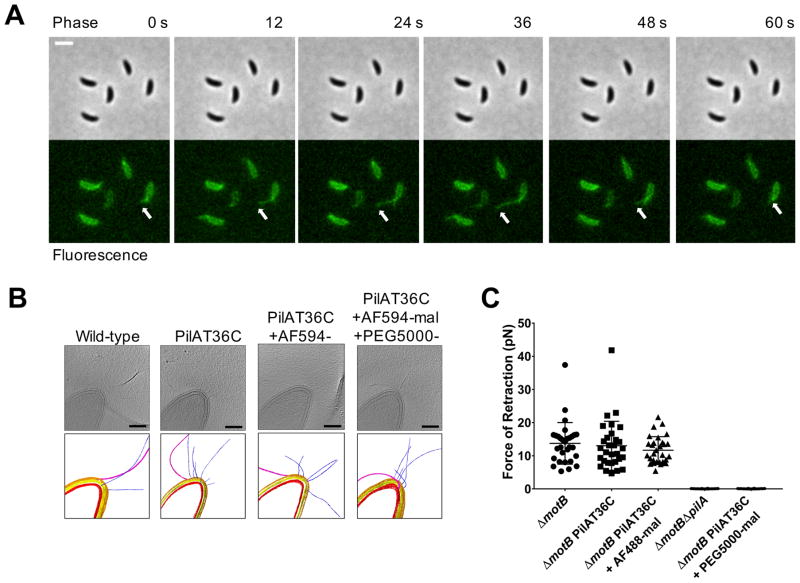
Figure 2. Tad type IVc pili undergo dynamic cycles of extension and retraction.
(A) Time-lapse of labeled, synchronized PilAT36C swarmer cells extending and retracting pili after labeling with AF488-mal dye. White arrow follows the most prominent extension and retraction event for a single cell, though all cells shown extend and retract pili. Scale bar is 2 μm. (B) Slices from tomograms and corresponding 3D segmentations of wild-type, PilAT36C, PilAT36 labeled with AF594-mal, and PilAT36C blocked with PEG5000-mal and labeled with AF594-mal. In 3D segmentation volumes, flagella are pink, pili are blue, S-layer is gold, outer membrane is yellow, and inner membrane is red. Scale bars are 200 nm. (C) Micropillars assay force measurements of retraction of tad type IVc pili in flagellar motor mutant ΔmotB strains. Flagellar motor mutants exhibiting paralyzed flagella were used to ensure all measurements obtained were dependent solely on pilus activity. Error bars show mean ± SD from 30 cells for each dataset.