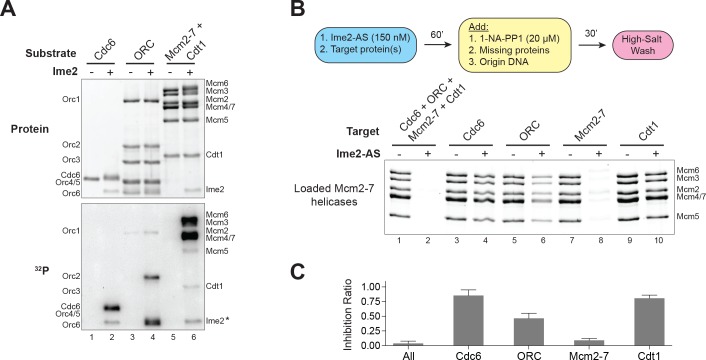
Figure 4. Ime2–phosphorylation of the Mcm2–7 complex intrinsically inhibits its loading onto replication origins.
(A) Ime2 can phosphorylate Cdc6, ORC, Cdt1 and Mcm2–7 in vitro. Buffer control (lanes 1, 3, and 5) or 50 nM Ime2 (lanes 2, 4, and 6) were incubated with the indicated substrate proteins. The substrates were purified Cdc6 (lanes 1 and 2), ORC (lanes 3 and 4) or Mcm2–7–Cdt1 (lanes 5 and 6). Asterisk (*) marks Ime2 autophosphorylation. Top: total protein (Krypton stain). Bottom: phosphorylated protein (modified with [γ-32P] ATP). (B) Ime2–phosphorylation of each protein separately shows that the primary target of Ime2–mediated inhibition is the Mcm2–7 complex (compare lanes 7 and 8). Top: Flowchart of experiment. Bottom: Helicase–loading assay after prior Ime2–phosphorylation of indicated protein. (C) Quantification of (B) from three independent experiments. Inhibition ratio was calculated as total Mcm2–7 loading from the +Ime2 reactions divided by amount of loading in the corresponding reaction lacking Ime2. The mean is represented by the height of the bar. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent experiments.