Fig. 1. CX3CR1 mononuclear cells express antifungal receptors and recognize fungi in the intestine.
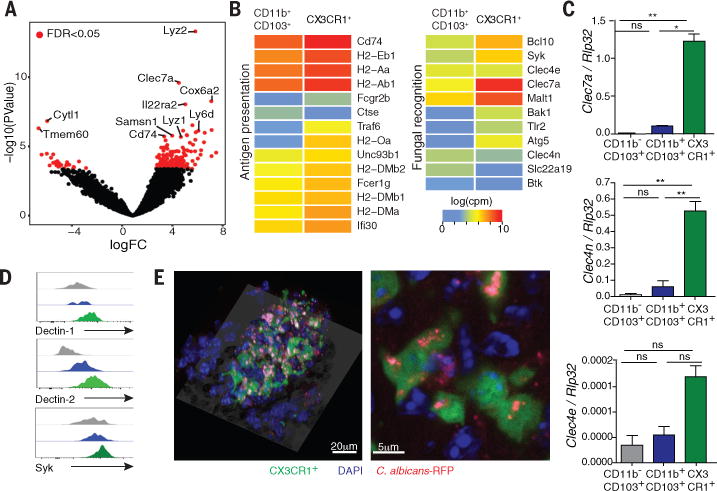
(A) RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis was performed on sorted CD11b+ CD103+ dendritic cells and CX3CR1+ mononuclear phagocytes. Volcano plot of P-value versus FC comparing gene expression in the two cell subsets; red dots indicate an FDR of <0.05. (B) Logarithmic count per million (log(cpm)) normalization of genes involved in antigen presentation (left panel) or fungal recognition (right panel). (C) The expression of antifungal CLRs was confirmed by RT-qPCR. (D) Representative flow cytometry histogram of dectin-1, dectin-2 and Syk expression among CD11b− CD103+; CD11b+ CD103+ and CD11b+ CX3CR1+ cells in colons of WT mice. (E) Representative confocal imaging of the intake of C. albicans-RFP (red) by CX3CR1+ MNPs (green, CX3CR1+, DAPI+) and other cell types (blue, CX3CR1−, DAPI+) in the intestine. Bar graphs represent mean ± SEM of individual mice (N=4-7), representative of at least two independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, one-way ANOVA.
