Figure 5. SAP mediated signaling in T cells regulates CD74 expression and B cell survival in vivo, and anti-CD4 downregulates SLAMF6 expression in vivo.
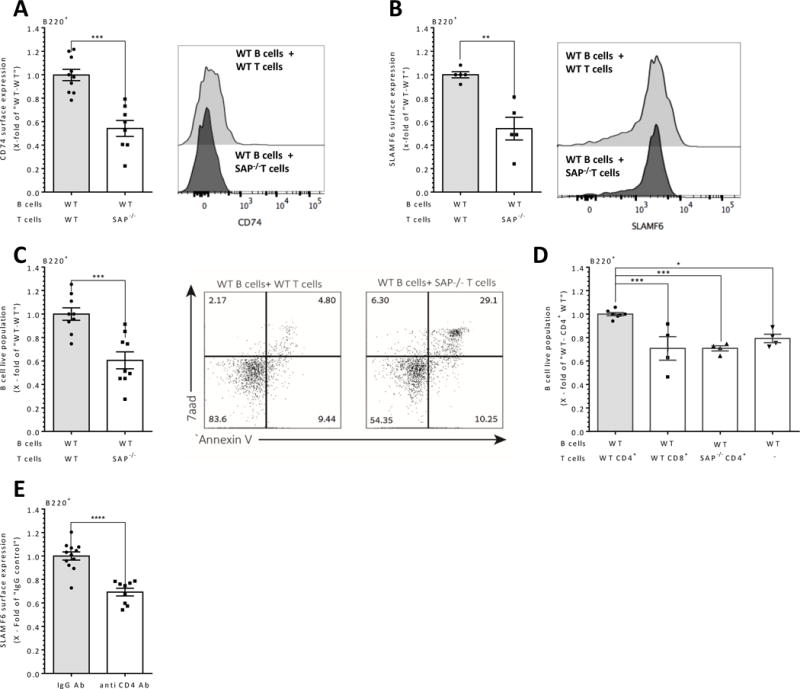
(A-D) Naïve wt B cells were injected into the tail vein of RAG1−/− mice together with 5×106 WT or SAP−/− T cells. After 24 hrs, splenocytes of RAG1−/− recipients were harvested and analyzed by flow cytometry for CD74. N=4. (A), right panel shows representative histograms of CD74 expression), SLAMF6. (B), right panel shows representative histograms of SLAMF6 expression) and Annexin V/7-AAD. N=3._ (C), right panel shows representative dot plots of Annexin V/7AAD). All results are shown as x- fold of “WT B cells and WT T cells”. (D) Naïve wt B cells were injected into the tail vein of RAG1−/− mice together with 5×106 WT or SAP−/− CD4+ or CD8+ T cells. After 24 hrs, splenocytes of RAG1−/− recipients were harvested and analyzed by flow cytometry for B cell survival. Results are shown as x-fold of “WT B cells and WT CD4+ T cells”. N=3. (E) WT mice were injected i.v. to the tail vein with 150 μg anti-CD4 neutralizing Ab or with PBS alone as control. After 4 days following the injection, PB was collected from the tail vein and analyzed for SLAMF6 expression on B cells. N=3. Results are shown as fold change relative to the control group, bars indicate SEM. In all results, each dot represents a biological repeat. N represents the number of experiments. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.
