Figure 4. Discovery of additional ORFs from PML brain tissue samples.
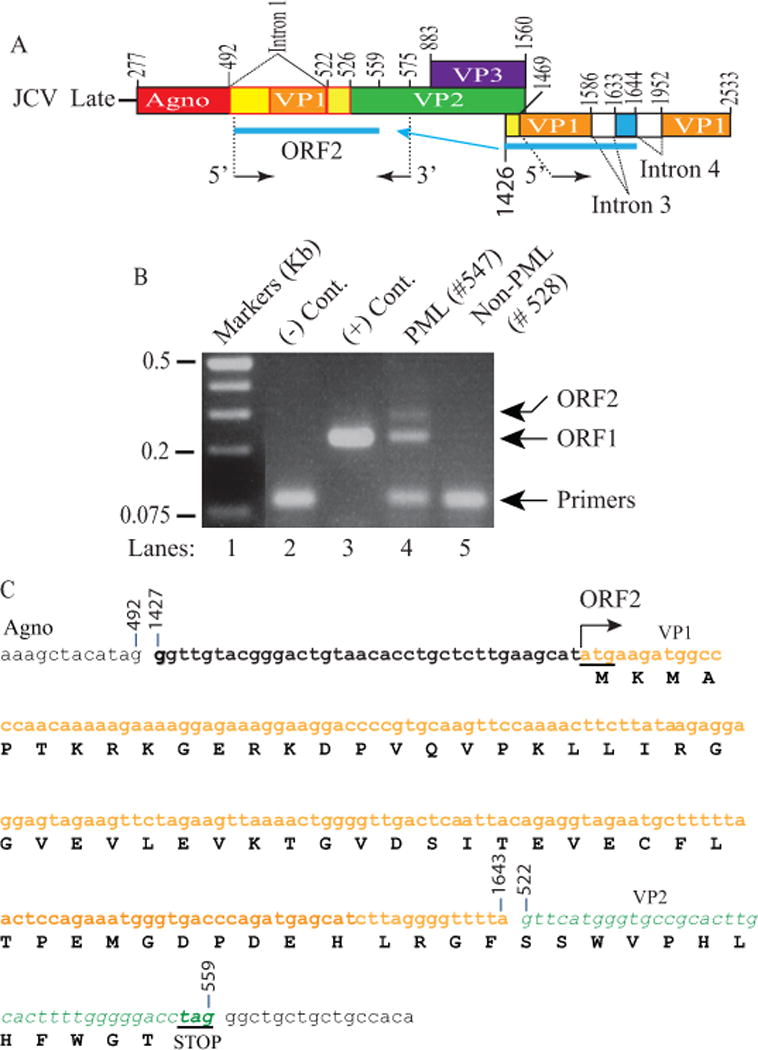
(A) Schematic representation of JCV late transcript containing the ORF2 coding region. (B) RT-PCR amplification of the ORF1 coding region with specific internal primers followed by analysis of the amplified products by agarose gel (3%) electrophoresis. Total RNA isolated from SVG-A cells [uninfected (-Cont., lane 2) and infected with JCV Mad-1 genome, (+ Cont., lane 3)]; and from PML (lane 4) and non-PML (lane 5) patients were subjected to RT-PCR using the following internal primers: 5′-primer: JCV Mad-1 VP1 (1469-1481), 3′-primer: JCV Mad-1 VP2 (575-555). The RT-PCR products were gel-purified and subcloned into XbaI/BamHI sites of the pCGT7 and sequenced. The sequencing data showed that, in addition to ORF1, a longer fragment of VP1 (216 bp) was also inserted in place of Intron 1 in another splice product creating another new ORF designated as a ORF2. Sequencing data also revealed that a mutant form of ORF1 also exists in PML tissue samples, designated ORF1M where Ile23 is mutated to Met (Ile23Met). (C) Schematic representation of a trans-spliced fragment (216 bp) of the 5′-end of the VP1 [Mad-1 (1427-1643) region] in place of “Intron 1” and creation of ORF2 (72 aa). After insertion, a frame shift occurs within VP2, which is terminated with a stop codon at nucleotide position 559. The common region of ORF1 (60 aa long) with VP1 is colored in orange and the unique region is colored in green (12 aa long).
