Figure 4. ETV4 transcriptionally upregulates cyclin D1 via direct binding to its promoter region.
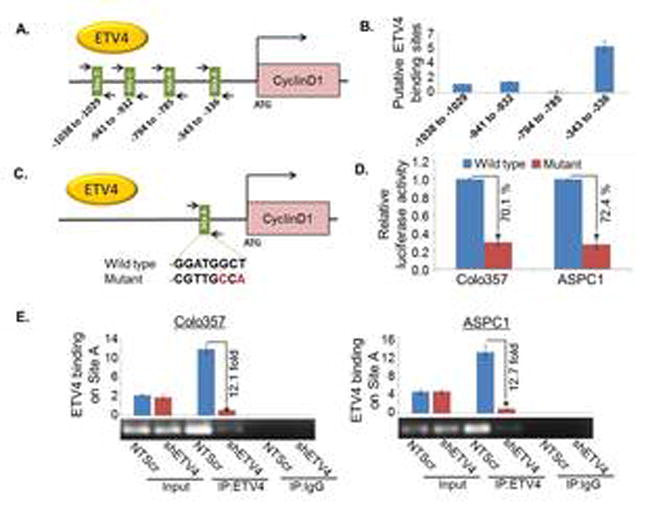
(A) Schematic diagram of human cyclin D1-promoter showing putative ETV4 binding sites. Arrows indicate the position and orientation of forward and reverse primers. The number below the bars represents the position of putative binding sites. (B) The direct binding of ETV4 to Cyclin D1 promoter was shown using ChIP assay. PCR was performed using specific primers as indicated. (C) Site A (-343 to -336) sequence 5′- GGATGGCT-3′ was mutated to 5′- CGTTGCCA -3′ using site-directed mutagenesis kit. (D) The wild type and mutated cyclin D1 promoter construct was transfected into PC cells and luciferase assay was performed 24h after transfection using the dual Luciferase Reporter Assay kit to determine the luciferase activity. (E) PCR amplification signal in low and high ETV4 expressing Colo357 and ASPC1 cells, suggesting the specificity of ETV4-dependent chromatin pull-down. Input DNA (without immunoprecipitation) and normal IgG-precipitated DNA were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. Bars represent mean ± S.D, n=3; *, (p<0.05).
