Fig. 2.
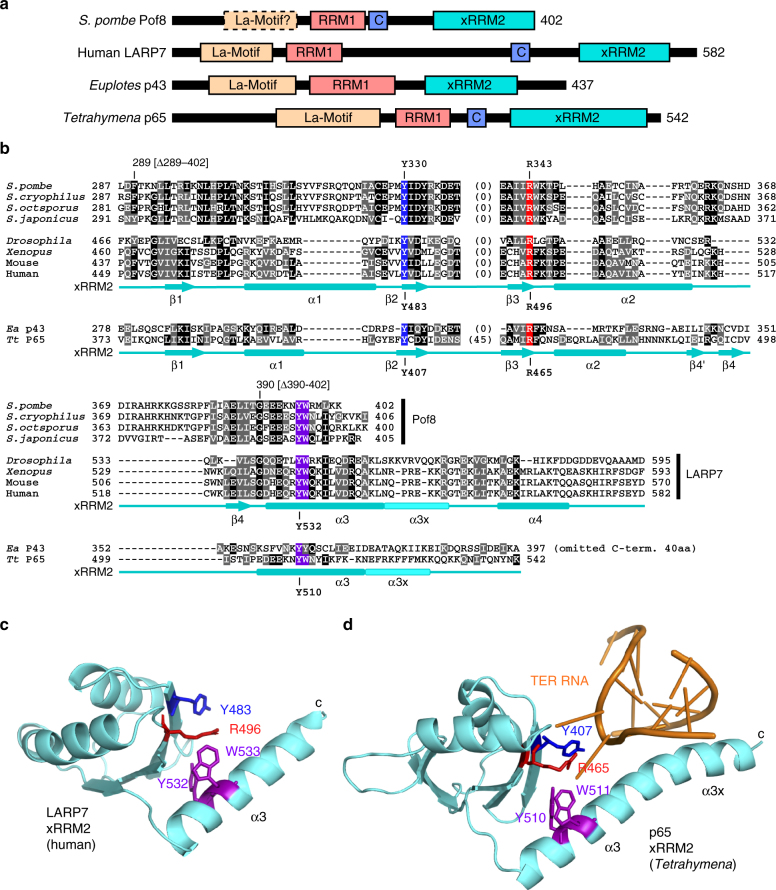
Fission yeast Pof8 shows similar domain organization as LARP7 family proteins. a Comparison of putative functional domains identified in S. pombe Pof8 to corresponding domains in human LARP7, Euplotes p43 and Tetrahymena p65 proteins. b Sequence alignment of xRRM2 domain from Pof8 proteins from Schizosacchromyces species (S. pombe, S. cryophilus, S. octsporus, and S. japonicus), LARP7 proteins (Drosophila, Xenopus, mouse, and human), Euplotes p43, and Tetrahymena p65. Highly conserved residues that have been implicated in RNA recognition33, 37, 47 are highlighted with colored background. Amino-acid residues that show at least 50% conservation among aligned sequences are highlighted in black (identical residues) or gray (similar residues, grouped as GAVLI, FYW, CM, ST, KRH, DENQ, and P). The secondary structures for human LARP747 and Tetrahymena p6537 are also indicated in cyan. Full length alignment of Pof8 from four fission yeast species, along with Pof8-like proteins from additional fungal species are shown in Supplementary Fig. 2. Sequence alignment of the N-terminal domain spanning the putative La-motif and RRM1 domains are shown in Supplementary Fig. 3a. c, d Structures of xRRM2 domains from (c) human LARP747 and (d) Tetrahymena thermophila p6537. Highly conserved amino acid residues are shown with same color as highlighted in (b). For LARP7, amino acid residues V455-N545 are shown (PDB ID: 5KNW). For p65, amino-acid residues C379-N412 and G461-K532 are shown (PDB ID: 4ERD). (Extra amino acid residues between N412 and G461 were deleted in the construct that was used in structure determination of p65-TER complex37.) Telomerase RNA shown in d corresponds to G118-U127 and A144-A148