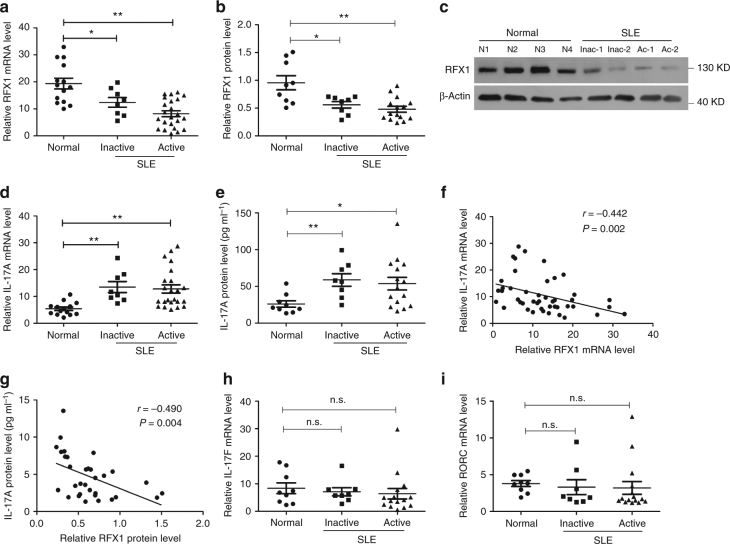
Fig. 1.
Decreased RFX1 and increased IL-17A expression in CD4+ T cells of SLE patients. mRNA (a) and protein (b) expression levels of RFX1 in CD4+ T cells of inactive SLE patients (n = 8), active SLE patients (n = 23 for mRNA and n = 15 for protein) and healthy subjects (n = 14 for mRNA and n = 9 for protein). Representative results of western blot analysis are shown in (c). IL-17A mRNA expression level in CD4+ T cells (d) and protein level in serum (e) of inactive and active SLE patients and healthy subjects. f Correlation between RFX1 and IL-17A at the mRNA level. g Correlation between RFX1 protein levels in CD4+ T cells and IL-17A protein levels in serum. h and i mRNA expression levels of IL-17F and RORC in CD4+ T cells of inactive SLE patients (n = 8), active SLE patients (n = 15) and healthy subjects (n = 9). Small horizontal lines indicate the mean (±s.e.m) in a, b, d, e, h, i. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; n.s., not significant, compared between the indicated groups. Student’s t-test (two-tailed) and Mann–Whitney U-test (two-tailed) were used to compare the results. Sperman’s correlation coefficient was used for the correlation analysis (two-tailed)