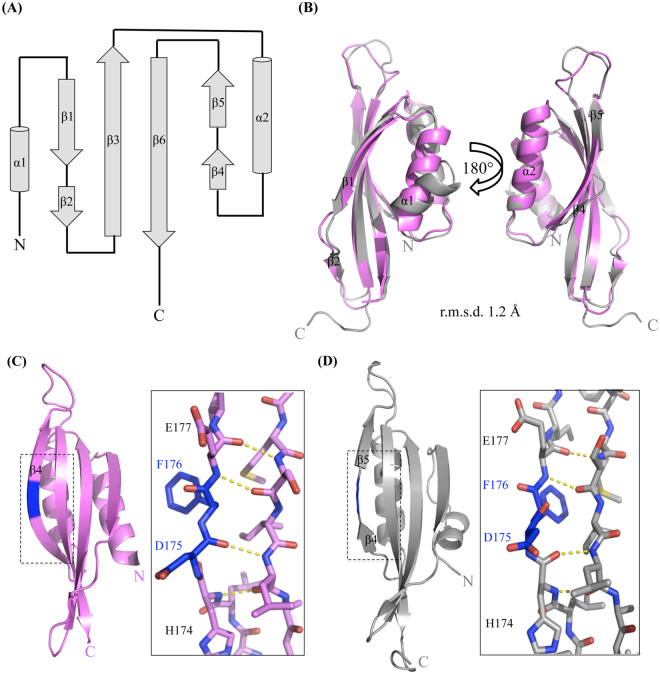
Figure 2.
Comparison of P. aeruginosa PilO structures. (A) Topological diagram of PilOΔ109 mapping the N- (P110) and C-termini (K206). Helices α1 and α2 are 8 and 13 residues in length, respectively, while β3 and β6 are 12 residues long. Beta strands β1 and β2 are 8 and 3 residues in length, whereas β4 and β5 have 3 and 4 residues, respectively. (B) Comparison of the PilOΔ109 structure (grey; PDB 5UVR) with the equivalent residues (110–206) of PilO2RJZΔ109 (violet; PDB 2RJZ30). (C) Reverse view of the PilO2RJZΔ109 structure (violet), highlighting the β4 strand residues, D175 and F176 (blue), participating in hydrogen bonding with the β5 strand. (D) The equivalent region of the PilOΔ109 structure (grey) highlighting the second discontinuous β4β5-strand (inset) and the D175 and F176 residues (blue) not participating in hydrogen bonding with the β6 strand. Hydrogen bonding is indicated by the yellow dashed lines.