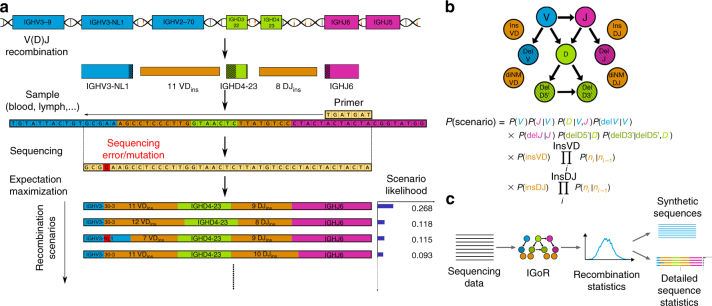
Fig. 1.
IGoR’s pipeline for sequence analysis. a V(D)J recombination proceeds by joining randomly selected segments (V, D, and J segments in the case of TRB and IGH). Each segment gets trimmed at its ends (hashed areas), and a varying number of non-templated insertions are added between them (orange). Hypermutations (in the case of B cells) or sequencing errors (in red) further enhance diversity. IGoR lists putative recombination scenarios consistent with the observed sequence, and weighs them according to their likelihood. b The likelihood of each scenario is computed using a Bayesian network of dependencies between the recombination features (V, D, J segment choices, insertions, and deletions), as illustrated here for the human TRB locus. Architectures for TRA and IGH are described in Methods. c IGoR’s pipeline includes three modes. In the learning mode, IGoR learns recombination statistics from data sequences. In the analysis mode, IGoR outputs detailed recombination scenario statistics for each sequence. In the generation mode, IGoR produces synthetic sequences with specified recombination statistics