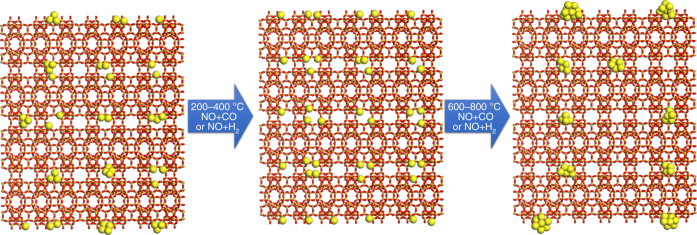
Fig. 7.
Structural evolution of Pt species under CO + NO and NO + H2 conditions. At 200–400 °C, Pt clusters will disintegrate and form highly dispersed Pt species. At higher temperature (600–800 °C), highly dispersed Pt species agglomerate into Pt clusters or even small Pt nanoparticles (1–2 nm). Due to the protection effect from MCM-22 framework, Pt clusters and small nanoparticles (1–2 nm) can be stabilized at such high temperature