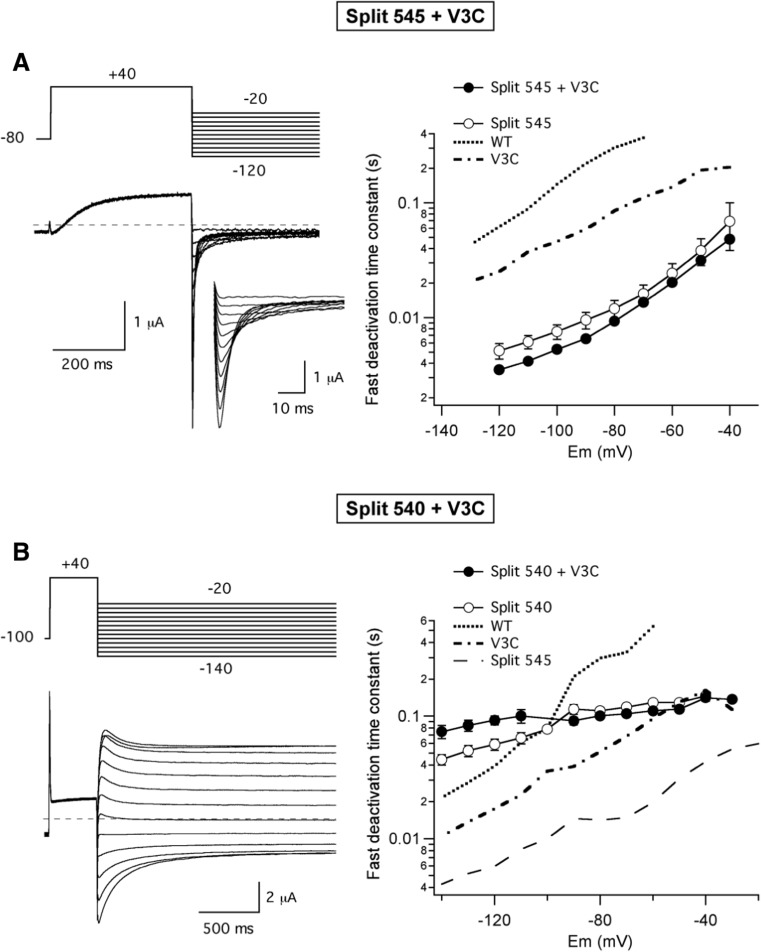
Fig. 5.
Deactivation kinetics of channels split at the beginning or the end of the S4–S5 linker are not modified by a mutation in residue 3 of the Kv11.1 N-tail. a Deactivation characteristics of split 545 channels carrying a V3C mutation in the N-tail of the N-terminal demi-channel. A representative family of currents is shown on the left, obtained with the protocol shown on top of the currents. A high-K+ extracellular solution was used to maximize the currents due to the small current magnitudes obtained with the split 545 + V3C construct (see “Materials and methods” section). Only the first part of the 4-s repolarization steps is shown. An expanded view of the initial part of the tails is shown in the inset. The dependence of deactivation rates on repolarization membrane potential is shown on the right. Only the magnitude of the deactivation time constant corresponding to the fast decaying major component of current at negative voltages is shown. Data from WT, the full-length V3C mutant and non-mutated split 545 channels also recorded in high-K+ are shown for comparison as indicated. b Deactivation characteristics of split 540 channels carrying a V3C mutation in the N-tail of the N-terminal demi-channel. A representative family of currents is shown on the left. The dependence of deactivation rates on repolarization membrane potential is shown on the right. Data from WT, full-length V3C and non-mutated split 540 and split 545 channels are also shown for comparison