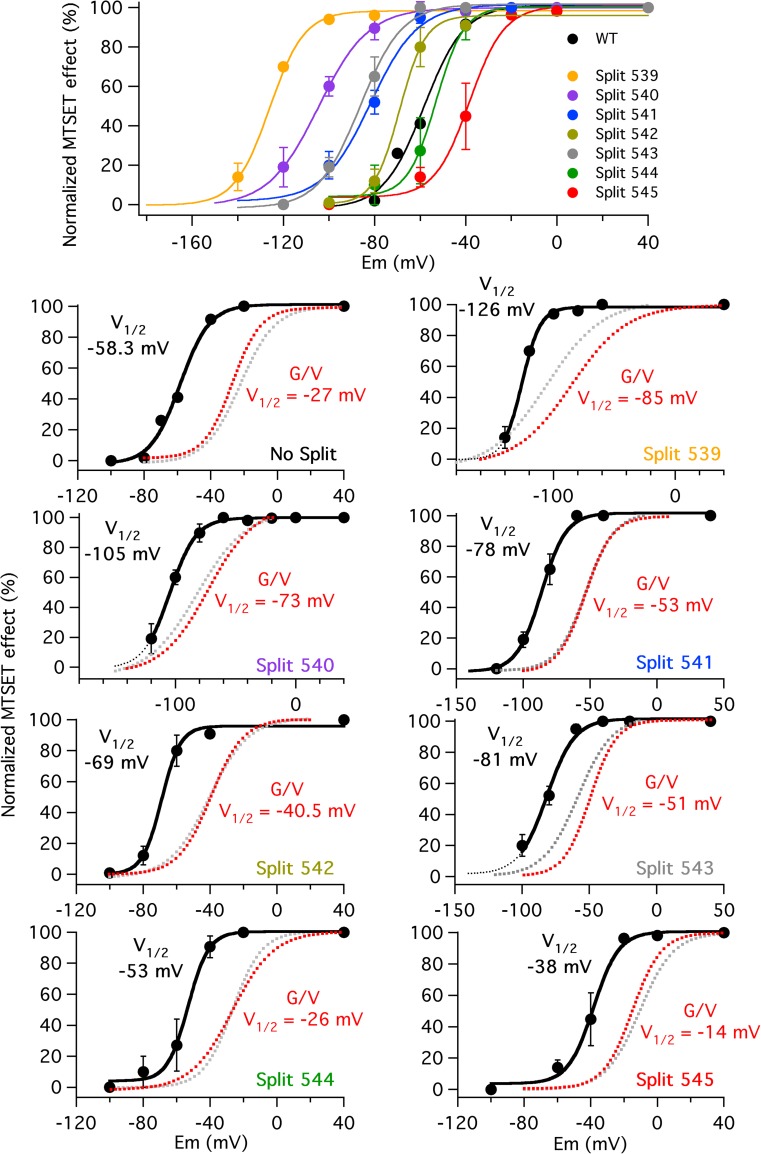
Fig. 7.
Effect of split position displacement on voltage dependence of MTSET availability to an engineered cysteine at position 521 in the extracellular part of the voltage sensor S4 helix. Summary of voltage dependence of the MTSET effect in different splits carrying the I521C mutation at the extracellular part of the voltage sensor S4 helix, as a function of the holding potential used during the MTS reagent exposure (upper panels). Plots of voltage dependence of the MTSET effect in the individual splits tested (lower panels). Magnitudes of MTSET-induced variations in current kinetics during test ramps as indicated in “Materials and methods” section following a 2-min exposure to 1 mM of the MTS reagent without pulsing at the holding potentials indicated in the abscissa were normalized to those observed at a positive potential value of + 40 mV. Due to the irreversibility of the MTSET effects, only one reagent application was performed and a single holding potential value (followed by a positive control at + 40 mV) was checked in each cell studied. Data from three to six cells were averaged for every single point. Some error bars are smaller than the symbols. Continuous lines correspond to fits using a Boltzmann function as indicated in “Materials and methods” section. The corresponding V 1/2 values are shown on the graphs. G/V plots from the same constructs obtained from fits to tail current data and V 1/2 values derived from them are also shown in red. Note the similarity of these plots and those from the same splits without the I521C plus C445V and C449V mutations (gray dotted lines; reproduced from Fig. 1d)