Figure 5.
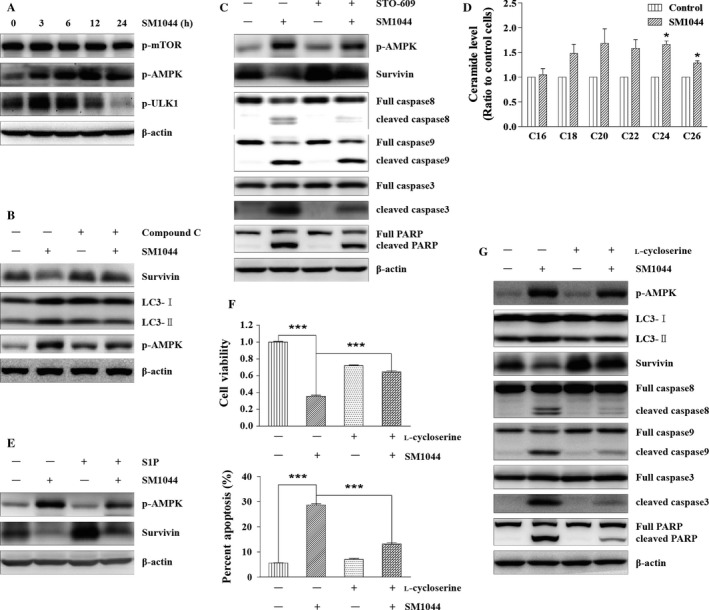
SM1044 induces CaMKK2–AMPK–ULK1 pathway‐mediated autophagy through promoting de novo synthesis of ceramide. (A) SU‐DHL‐4 cells were treated with SM1044 for the indicated time courses. The active ULK1, AMPK and mTOR were detected by western blot. (B) SU‐DHL‐4 cells were pretreated with AMPK inhibitor compound C for 1 h, followed by SM1044 treatment for another 24 h. The levels of LC3, Survivin, and p‐AMPK were detected by western blot. (C) SU‐DHL‐4 cells were pretreated with CaMKK2 inhibitor STO‐609 for 1 h, followed by SM1044 treatment for another 24 h. The levels of p‐AMPK, Survivin, caspase‐8, ‐9, ‐3, and PARP were detected by western blot. (D) SU‐DHL‐4 cells were treated with SM1044 for 3 h and the level of ceramide was detected by HPLC‐MS/MS. C24: Control versus SM1044, P = 0.011. C26: Control versus SM1044, P = 0.023. (E) SU‐DHL‐4 cells were pretreated with ceramide inhibitor S1P for 1 h, followed by SM1044 treatment for another 24 h. The levels of p‐AMPK and Survivin were detected by western blot. (F) SU‐DHL‐4 cells were pretreated with ceramide de novo synthesis inhibitor l‐cycloserine for 1 h, followed by SM1044 treatment for another 24 h. Cell viability was detected by CCK‐8 (upper panel, mean ± SEM, n = 3) and apoptosis was measured by flow cytometry (lower panel, mean ± SEM, n = 3). Cell viability: SM1044 versus control, P < 0.001, SM1044 versus l‐cycloserine plus SM1044, P < 0.001. Percent apoptosis: SM1044 versus control, P < 0.001, SM1044 versus l‐cycloserine plus SM1044, P < 0.001. (G) SU‐DHL‐4 cells were pretreated with l‐cycloserine for 1 h, followed by SM1044 treatment for another 24 h. The levels of p‐AMPK, LC3, Survivin, caspase‐8, ‐9, ‐3, and PARP were detected by western blot. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001.
