Figure 4. Stages of HF induction recapitulated in Atoh1/nGFP mESCs and miPSCs. See also Figure S4.
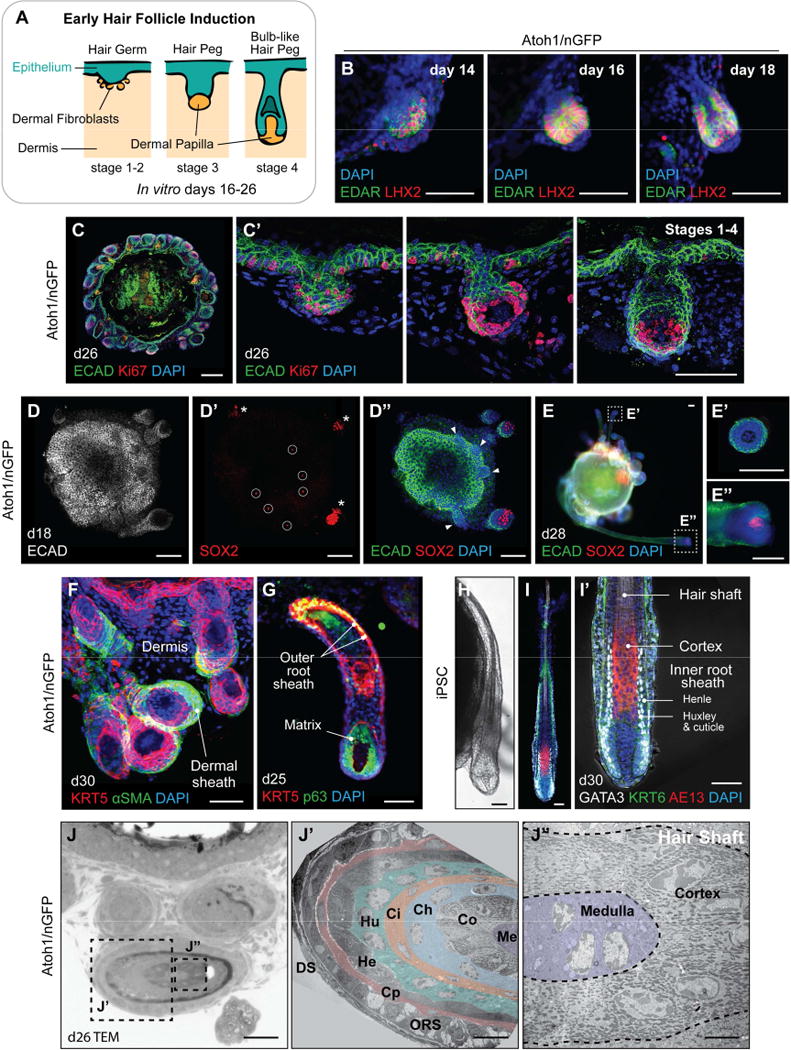
A, Illustration of the first four of eight stages of native HF development: hair germ, peg, and bulb formation. B, Representative IHC images of EDAR+ LHX2+ developing hair germs on days 14, 16, and 18. C, C′, Ki67+ cells in the hair germ and nascent HF matrix epithelium on day 26. Day 26 organoid contains HFs at different developmental stages (hair germs, pegs, and bulb-like hair pegs) in a single organoid unit. D–D″, Day 18 skin organoid contains HFs with SOX2+ DP (D′, *) and SOX2− germ stage HFs (D″, arrowheads). Sparse SOX2+ interfollicular epithelial cells represent Merkel cells (D′, circles). See also Figure 5F–F″. E–E″, On day 28, skin organoids have HFs containing or lacking SOX2+ DP; HFs with SOX2− DP suggest a zigzag HF identity (E′), while HFs with SOX2+ DP suggest guard, awl, or auchene HF identity (E″). F–I′, Representative images of developing HFs showing (F) αSMA+ dermal sheath cells, (G) KRT5+ p63+ outer root sheath and p63+ matrix cells. (H) Representative DIC image of an iPSC-derived HF on day 30. (I, I′) GATA3+ inner root sheaths comprised of Huxley’s and cuticle layers with Henle’s layer, distinguishable by morphology. AE13+ cells were located in the hair cortex region of organoid HF shafts. J–J″, TEM images of the Atoh1/nGFP ESC-derived skin organoid HF on day 26. (J′) Cross-section of the hair shaft showing HF lineages. From the outermost layer to the center of the HF: DS, dermal sheath; ORS, outer root sheath; Cp, companion layer; He, Henle’s layer; Hu, Huxley’s layer; Ci, inner root sheath cuticle; Ch, hair shaft cuticle; Co, cortex; Me, medulla. (J″) High magnification view of the cortex and medulla. Dash-lined boxes (E, J) indicate the area of magnification. Scale bars, 100 µm (B, C, D–E″), 50 µm (C′, F–I′, J), 10 µm (J′), 5 µm (J″).
