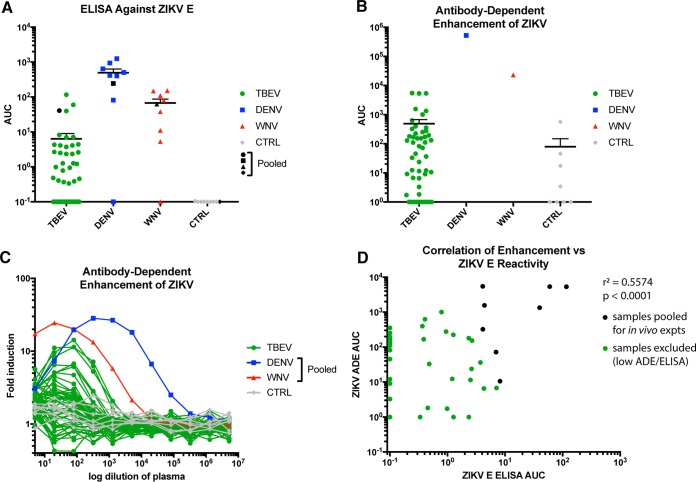
FIG 2 .
Anti-TBEV serum reacts to ZIKV E and enhances ZIKV infection in vitro. (A) AUC values from ELISAs against ZIKV E. Shown in blue are a preselected set of anti-DENV samples, with a range of reactivity. Shown in red are a similarly preselected set of anti-WNV samples. In gray are 8 naive-control (CTRL) plasma samples. In black for each are the pooled stocks used for later animal experiments. (B) AUC values derived from ADE in vitro experiments using ZIKV strain PRVABC59/2015 in K562 cells. DENV and WNV are plasma pools, as described for panel A. Naive-control samples are the same 8 samples employed to obtain the results shown in panel A. Lines represent geometric means. Error bars represent the standard errors of the means (SEM). (C) Raw ADE induction values derived from flow cytometry of K562 cells infected with ZIKV and incubated with the indicated serum/plasma sample. AUC values shown in panel B are based on this data. AUC values were calculated using all values up to the peak value for each curve. (D) Correlation analysis between ZIKV E ELISA AUCs and in vitro ADE AUCs. Each point represents one donor. r2 = 0.5574, P < 0.0001.