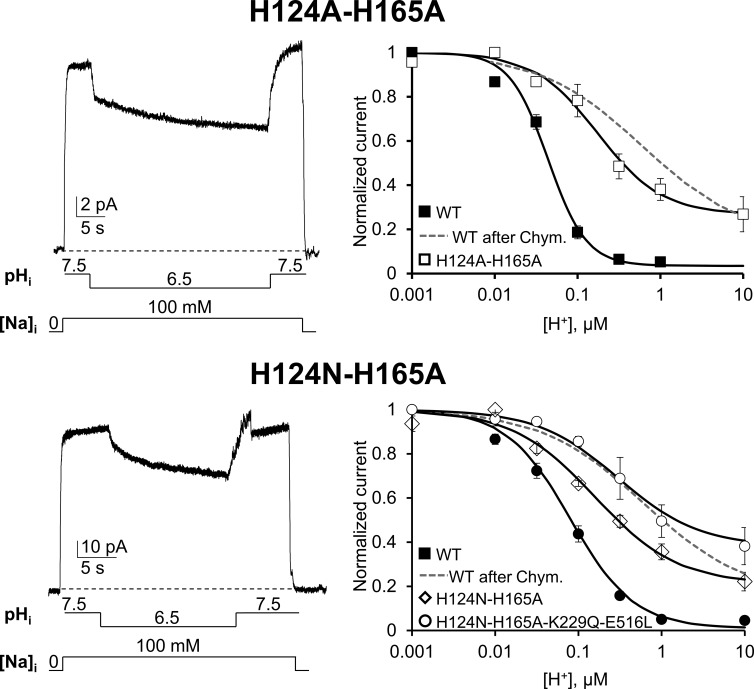
Figure 6.
His 124 and His 165 alter NCX pH regulation independently of their effects on Na+ and Ca2+ regulation. Recording of outward currents from oocytes expressing the indicated mutants. Normalized currents are plotted as function of proton concentration and shown on the right. Mutants H124A-H165A and H124N-H165A showed a further decrease in pH sensitivity when compared with the single mutants (see Fig. 5), with ∼25% of activity still present at 10 µM H+, pH 5. Introduction of mutations H124N-H165A in an exchanger lacking both Na+ and Ca2+ regulation (K229Q-E516L) did not prevent the decrease in proton sensitivity showing a H+ dependence as H124N-H165A (P > 0.0025; compare ○ with ♢). These results indicate that His 124 and His 165 alter NCX pH sensitivity independently from their effects on Na+ and Ca2+ regulation. Identical results were obtained with mutant H124N-H165A-K229Q (not depicted; see Fig. 4 for K1/2 value). The proton sensitivity of WT before (■) and after (gray dashed line) chymotrypsin deregulation is shown for comparison. Error bars represent SEM.