Figure 3.
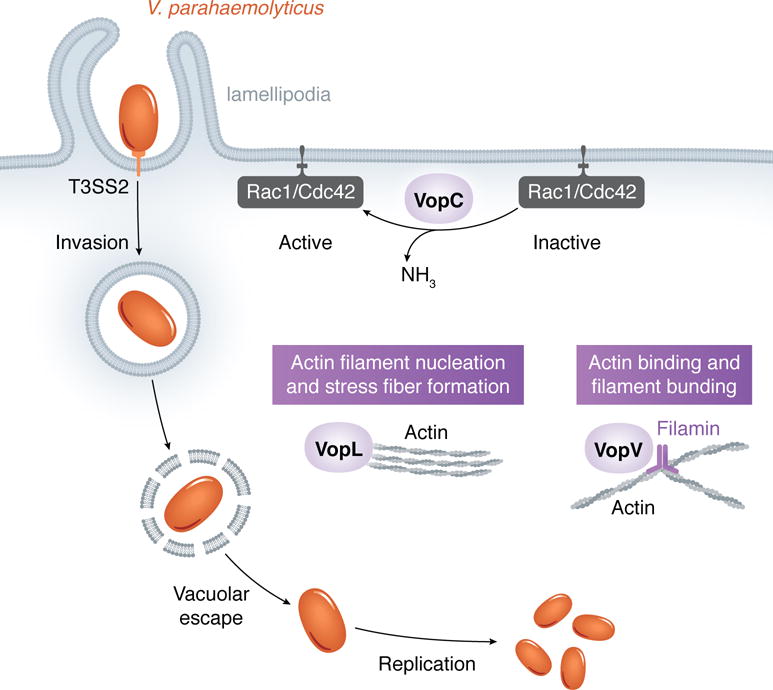
V. parahaemolyticus uses its T3SS2 effector VopC to activate Rac1 and Cdc42, which induce actin polymerization to cause bacterium entry into the host cell. V. parahaemolyticus then escapes its vacuole and replicates in the host cytosol. While VopL nucleates new actin filaments, VopV binds to and bundles actin filaments, their role in bacterial invasion and/or intracellular survival remains to be understood.
