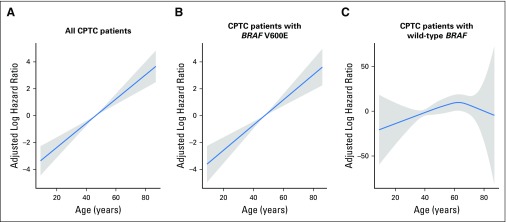
Fig A2.
Multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis of conventional papillary thyroid cancer (CPTC)–specific mortality risk with adaptive smoother splines: (A) all CPTC patients; (B) CPTC patients with BRAF V600E mutation; and (C) CPTC patients with wild-type BRAF. The blue line represents the fitted line of the association between patient age and the estimated hazard ratio (HR) of mortality risk after adjustment; the shaded region represents the 95% CI. The models were adjusted for the following clinicopathologic characteristics: patient sex, tumor size, extrathyroidal extension, lymph node metastasis, distant metastases, administered activities of radioactive iodine, and study center. Because of the small number of deaths in patients younger than age 45 years, there were large variations in log HRs in patients with CPTC harboring only wild-type BRAF in the young age ranges. Consequently, different y-axis scales are used for log HR for panels A, B, and C.