Figure 5.
Constant Association Is Necessary for L. plantarum-Mediated Drosophila Growth
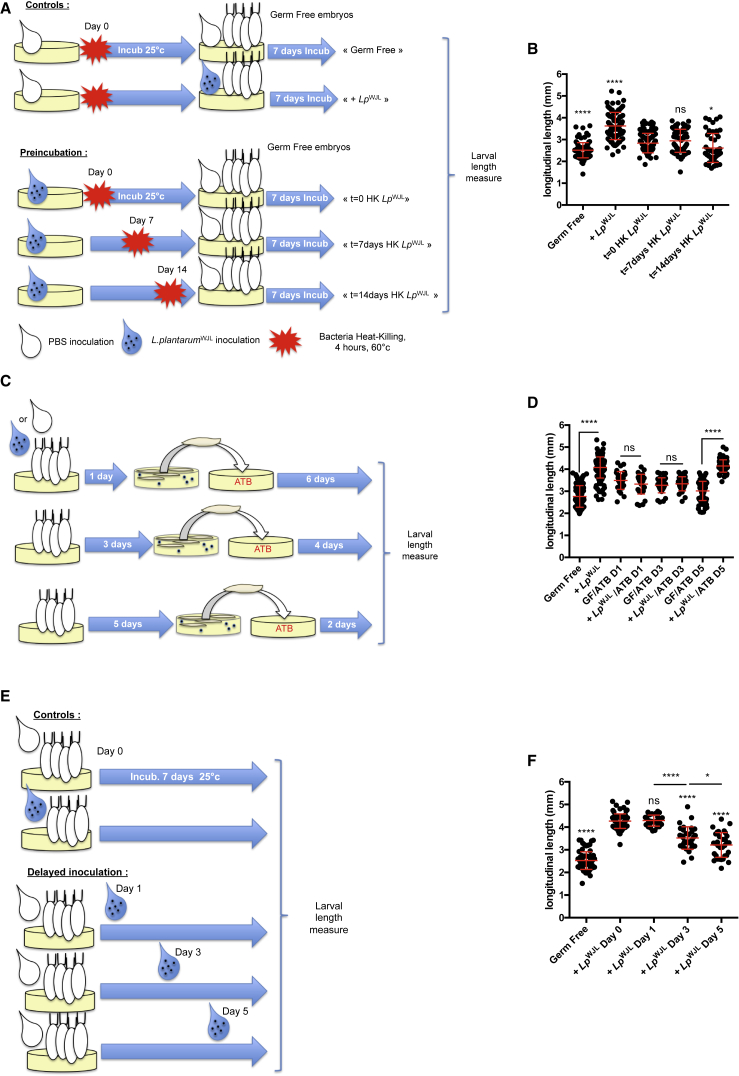
(A) Experimental setup to assess the impact of diet pre-incubation with bacteria on larval growth.
(B) Larval longitudinal length at D7 AEL after rearing on pre-incubated diets. Asterisks represent statistically significant differences with the pool of larvae reared on PYD where bacteria were immediately killed after inoculation (t = 0 HK LpWJL).
(C) Experimental setup to assess the impact of the timing of bacterial ablation on larval length gain after mono-association.
(D) Larval longitudinal length at D7 AEL after transfer on ATB-containing PYD. Efficient bacterial inactivation by ATB was assessed by plating larval homogenates at the time of collection on Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS) agar plates. Larval bacterial loads were evaluated to 0 CFU per larva for +LpWJL/ATB D1 and +LpWJL/ATB D3 and 19.3 CFU/larva for +LpWJL/ATB D5. Asterisks represent statistically significant differences between GF and mono-associated larvae pools transferred at the same time on ATB-containing PYD.
(E) Experimental setup to assess the impact of delayed mono-association on larval length gain.
(F) Larval longitudinal length at D7 AEL on PYD. Axenic embryos were mono-associated following the standard procedure (+LpWJL D0), or mono-association was delayed (D1, D3, and D5 AEL). Asterisks represent statistically significant differences with the pool of larvae mono-associated at D0 AEL. Asterisks above horizontal bars represent statistically significant differences between two conditions.
Asterisks illustrate statistical significance between conditions: ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, ∗p < 0.05, ns, not significant (p > 0.1).