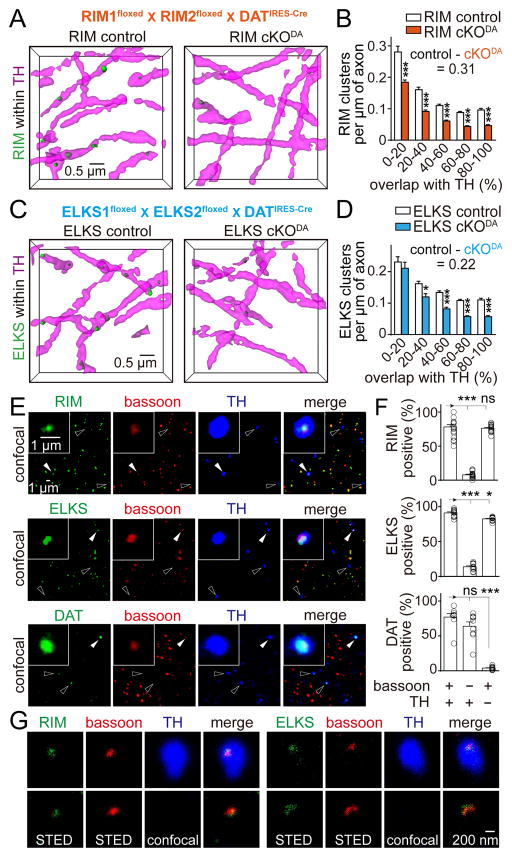
Figure 2. Bassoon, RIM and ELKS co-cluster in dopamine axons.
(A) Representative surface rendered images (5 × 5 × 2 μm3) of RIM clusters within dopamine axons from RIM control and RIM cKODA mice, in which RIM is removed specifically in dopamine neurons by breeding conditional RIM1 and RIM2 knockout mice to DATIRES-Cre mice (Figure S2). RIM control mice were siblings that lack Cre.
(B) Histogram of RIM cluster densities within dopamine axons across 20% bins of overlap. RIM control n = 24 regions/4 mice, RIM cKODA n = 22/4 (p < 0.001 for genotype, p < 0.001 for overlap, and p < 0.01 for interaction; two-way ANOVA, p-values of pairwise post tests indicated in figure). For detailed sample images and data analyses including shuffling, see Figure S2.
(C, D) Same as (A) and (B), except showing representative images (C) and quantification (D) of ELKS clusters in ELKS control and ELKS cKODA mice. ELKS control n = 29/4, ELKS cKODA 27/4 (p < 0.001 for genotype, p < 0.001 for overlap, and p = 0.37 for interaction; two-way ANOVA, p-values of pairwise post tests indicated in figure). For detailed sample images and data analyses including shuffling, see Figure S3.
(E) Confocal images of striatal synaptosomes. Filled arrowheads indicate synaptosomes containing bassoon and TH (insets). Hollow arrowheads indicate particles containing TH but not bassoon.
(F) Quantification of the percentage of synaptosomes that contain RIM, ELKS or DAT in three different types of synaptosomes, defined by specific markers as indicated below the plots. Each circle represents the average result of an area with 1,500–6,000 synaptosomes. n = 18 areas/3 mice for RIM, 12/3 for ELKS and 9/3 for DAT.
(G) Representative STED images of RIM (left) and ELKS (right) in synaptosomes co-labeled with bassoon in TH positive (top) and TH negative (bottom) synaptosomes.
All data are mean ± SEM. *** p < 0.001, * p < 0.05, ns, not significant; two-way ANOVA for (B, D) and Kruskal-Wallis analysis of variance with post hoc Dunn’s test for (F).