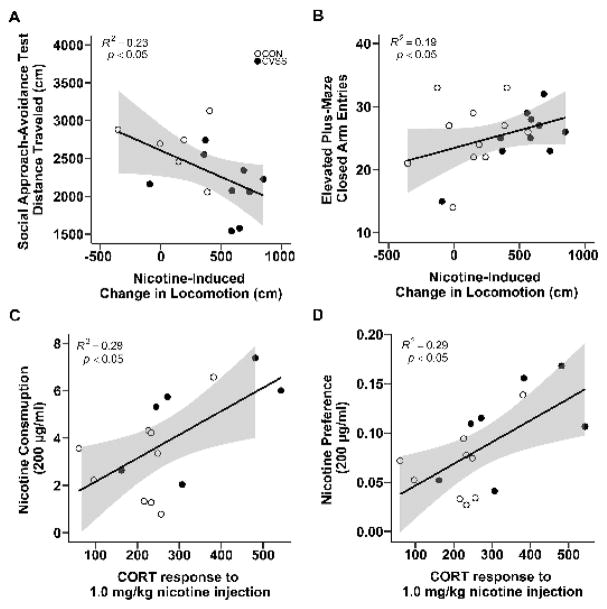
Figure 7.
Correlations between nicotine responses and exploratory behavior in the social approach-avoidance test and EPM in male mice. Nicotine-induced locomotor activity during late adolescence was (A) negatively correlated with distance traveled in the social approach-avoidance (N = 15) and (B) positively correlated with closed arm entries in the EPM during adulthood (N = 21). Plasma CORT response to 1.0 mg/kg nicotine was positively correlated with (C) consumption (N = 16) and (D) preference for 200 μg/ml nicotine (N = 16). The shaded regions signify 95% confidence intervals.