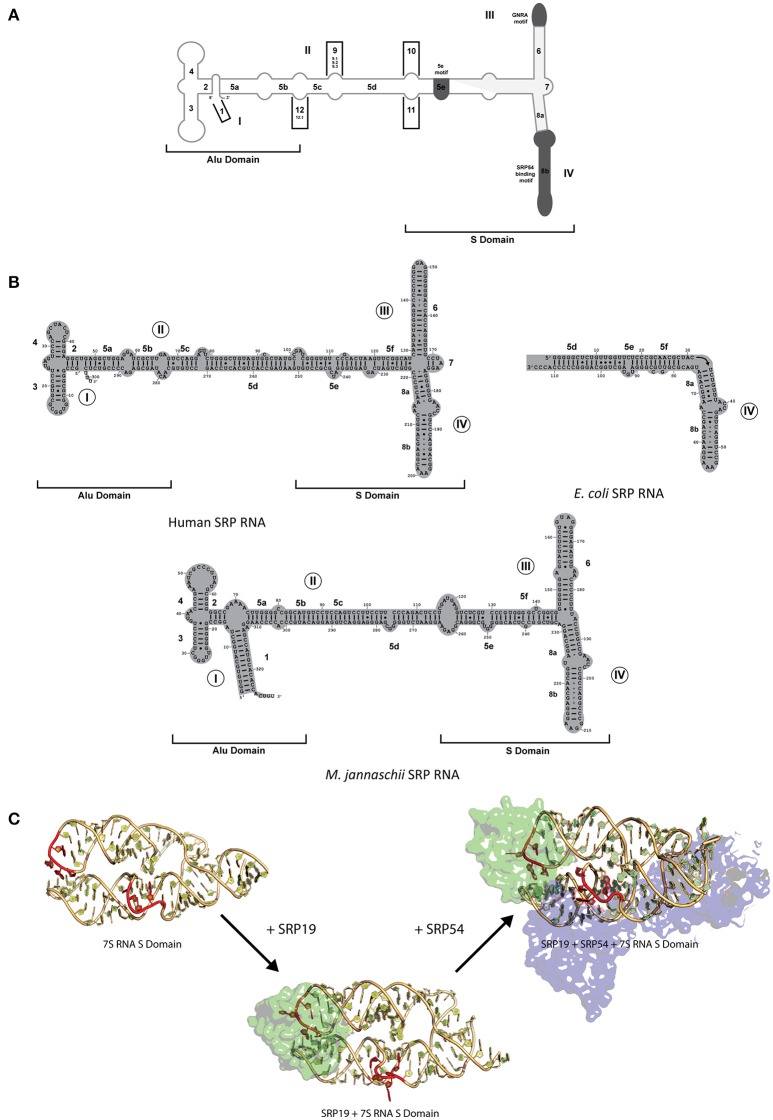
Figure 2.
SRP RNA secondary structures and conformational changes during SRP RNP formation. (A) SRP nomenclature. Mammalian SRP RNA secondary structure is traced in gray. Common motifs and helices are colored in dark gray. Helices are numbered 1–12 with helical sections labeled a–f. Domains are labeled I–IV. The approximate boundaries of the Alu domain and S domain are labeled. 5′ and 3′ ends are indicated (B) Secondary structures or the eukaryotic, bacterial and archaeal SRP RNA. Examples are shown of the eukaryotic (human), bacterial (Escherichia coli), and archaeal (Methanococcus jannaschii). Helices are numbered 1–8 with helical sections labeled a–f. Residues are numbered in increments of 10. Domains are labeled I–IV. The approximate boundaries of the Alu domain and S domain of the eukaryotic and archaeal SRP RNAs are labeled. 5′ and 3′ ends are indicated. (C) RNA conformational changes upon SRP complex formation in M. jannaschii. Crystal structure of apo 7S RNA of the S domain is shown (PDB: 1Z43). Crystal structures of SRP19 and 7S RNA S domain (PBD: 1LNG) and SRP19 and 7S RNA S domain (PBD: 2V3C) are shown. RNA conformational changes upon SRP19 binding and subsequent binding of SRP54 are shown in red.