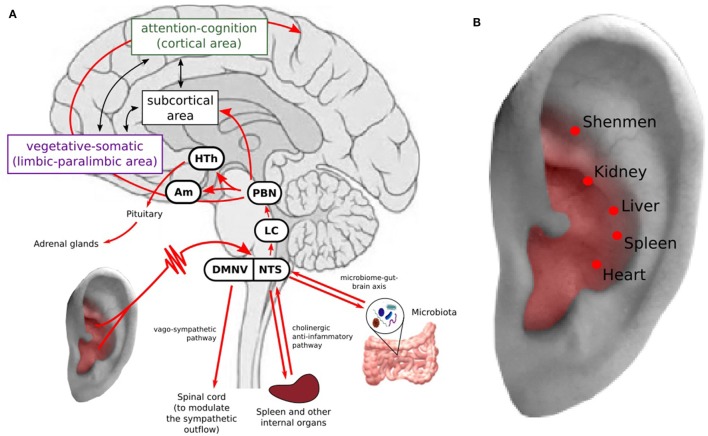
Figure 1.
(A) Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (taVNS) can modulate the brain network associated with the neuropathology of depression and inhibit inflammation response. Stimulation of the auricular branch of the vagus nerve (VN, indicated in red), which projects to the nucleus tractus solitari (NTS), continuing to the locus coeruleus and parabrachial nucleus. From the parabrachial nucleus, it propagates to various brain regions involved in depression (39, 40). taVNS may inhibit inflammation response to relieve stress and depressive symptoms. HTh, hypothalamus; PBN, parabrachial nucleus; LC, locus coeruleus; NTS, nucleus tractus solitary; DMNV, dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve. (B) Auricular acupuncture points used for treating depression and other mental disorders at area with VN distribution.