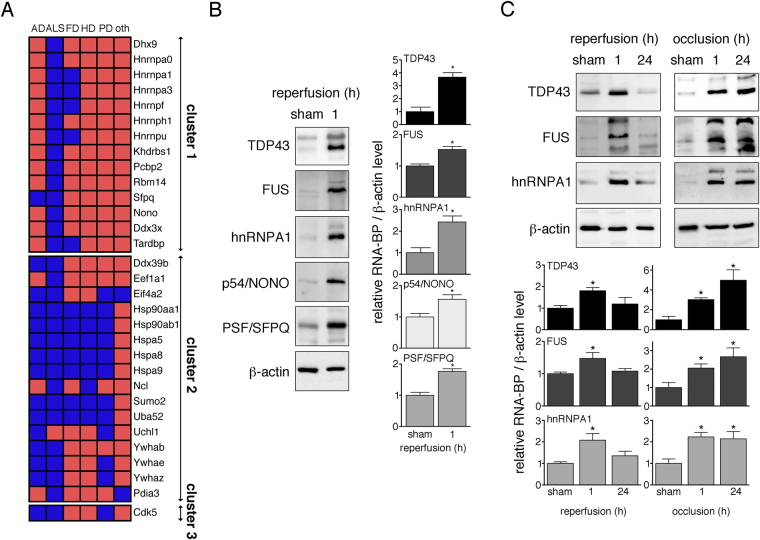
Figure 2.
Ischemic stroke induces the aggregation of the ALS- and FTD-related RNABPs TDP43, FUS, hnRNPA1, PSF/SFPQ and p54/NONO. (A) I/R-derived aggregated proteins were analyzed for their known ability to form aggregates in neurodegeneration. Identified proteins were clustered according to analysis in Fig. 1D. The heatmap points out disease affiliation of aggregate-prone proteins in ND, where blue boxes indicate positive and red boxes negative hits. AD, Alzheimer’s disease; ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; FD, frontotemporal dementia; HD, Huntington’s disease; oth, other; PD, Parkinson’s disease. (B) Triton-insoluble fractions were obtained from ipsilateral neocortical tissue from mice subjected to sham surgery or MCAO followed by 1-hour reperfusion. The presence of the RNABPs TDP43, FUS, hnRNPA1, p54/NONO and PSF/SFPQ in Triton-insoluble fractions was detected by Western Blotting with respective antibodies. Optical densities of RNABP bands were measured and normalized to β-actin. Changes in RNABPs were expressed relative to sham controls. *P < 0.05 from sham; n = 9/group. (C) Ipsilateral neocortices from sham animals, after MCAO followed by 1 and 24 hours reperfusion, or after 1 and 24 hours permanent MCAO were harvested. Triton-insoluble proteins were isolated and examined for the presence of TDP43, FUS and hnRNPA1 by Western Blotting. Quantification of results was carried out as in Fig. 2B. Full-size blots are presented in Supplementary Figures S2 and S3. *P < 0.05 from sham; n = 3–6/group. h, hours.