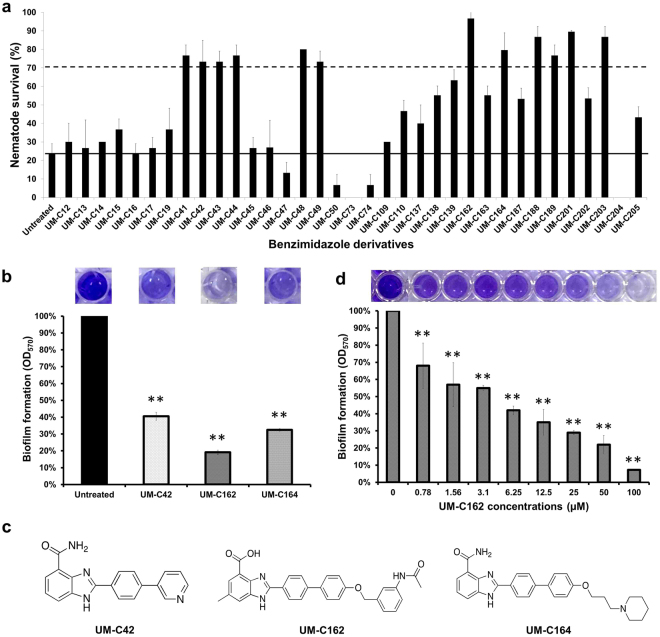
Figure 1.
Benzimidazole derivatives rescued C. elegans from a S. aureus infection and altered S. aureus biofilm formation. (a) Survival of S. aureus-infected nematodes upon treatment with individual benzimidazole compounds (100 µM). Results are shown as mean ± SD from a single replicate of two independent screens. The straight line shows the survival of untreated worms while the dashed line demarcates the positive hits. Compounds that promoted the survival of infected worms to > 70% were considered as positive in the screen. (b) Effect of benzimidazole compounds (100 µM) towards S. aureus biofilm formation. (c) Molecular structures of compounds UM-C42, UM-C162 and UM-C164 that demonstrated significant anti-biofilm activity. (d) Dose-dependent anti-biofilm effect of compound UM-C162. The graphs in (b) and (d) depict the percentage of biofilm formation after 24 hours incubation of S. aureus in the presence and absence of compounds. Three independent experiments were conducted. Error bars indicate SEM. Images of representative wells from the crystal-violet biofilm assay are shown. (**) denotes significant difference between untreated and compound-treated bacteria (p < 0.01).